Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ What must be added to f(x) = 4x^4 2x^3 2x^2 x 1 so that the resulting polynomial is divisible by g(x) = x^2 2x 3?I honestly have no idea how to this An example or helping me get through the problem would be great ) Thank you so much )G (x) = (a b − x 1 / 3 ) 1 / 2 Let g ( x ) be f − 1 x as f ( f − 1 ( x ) ) = x and f − 1 ( f ( x ) ) = x 3 y = a x 2 b ⇒ x 2 = a 3 y − b

If F X X 2 And G X 2x Then Evaluate I F G 3
F(x)=x^2 what is g(x) (3 3) brainly
F(x)=x^2 what is g(x) (3 3) brainly- · f (x) = 2x^2x3 g (x) = x 1 (f*g) (x) = f (x)*g (x) = (2x^2 x 3)* (x 1) = 2x^3 x^2 3x 2x^2 x 3 = 2x^3 x^2 4x 3 All real numbers can be plugged into this function, so its domain is that of all real numbers 👍 · 1 What is (f−g) (x)?



How Do You Find The Area Between F X X 2 2x 1 G X 3x 3 Socratic
Example f R ⇥ R where f(x) = x2 is not onetoone because 3 ⌅= 3 and yet f(3) = f(3) since f(3) and f(3) both equal 9 Horizontal line test If a horizontal line intersects the graph of f(x) in more than one point, then f(x) is not onetoone The reason f(x) would not be onetoone is that the graph would containExample 4 We wish to translate the graph of the function f(x) = x 3 – x by the vector The following table of values is for x taking values between –2 and 2 First we calculate f(x) Next we move all the outcomes down by 1 ( eg the value for x = – 2 becomes the value for x = –1)Simple and best practice solution for g(x)=x3 equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework If it's not what You are looking for type in the equation solver your own equation and let us solve it
F − 1 (3) = 2 3 Explanation Given, f (x) = lo g 3 (x 4) We must first determine the inverse of How do you solve \displaystyle{{\log}_{{{3}}}{\left({5}{x}{2}\right)}}={3} ? · What is (f x g)(x) f(x)= x^22x3 g(x)= x^34 Answers 1 Get Other questions on the subject Mathematics Mathematics, 15, emmanuel180 Can (3,5 and square root 34) be sides on a right triangle?More formally, f = g if f(x) = g(x) for all x ∈ X, where fX → Y and gX → Y The domain and codomain are not always explicitly given when a function is defined, and, without some (possibly difficult) computation, one might only know that the domain is contained in a larger set
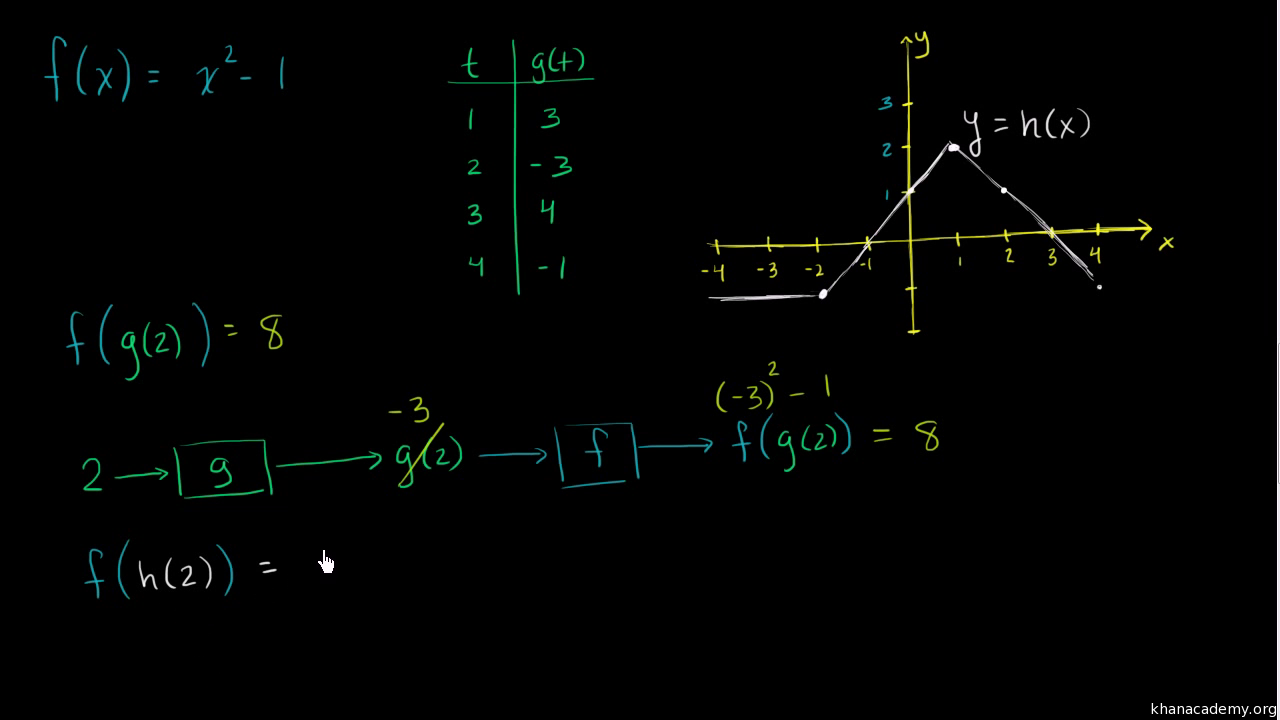
324 Describe three conditions for when a function does not have a derivative;The function g(x) is a translation of f(x) = (x 3)2 10 The axis of symmetry of g(x) is 5 units to the right of f(x) Which function could be g(x)?F(x) = 2x1 g(x) = x^23 Find value of g(f(1)) Solution First f(1) = 2*(1) 1, = 3 Now g(3) = (3)^2 3 g(3) = 9 3 g(3) = 12 Answer is 12




Pls Help If F X 3 5x And G X 3x 2 Find F X G X Brainly Com



How Do You Find The Area Between F X X 2 2x 1 G X 3x 3 Socratic
· If the function f (x) = x^3 e^x/2 and g (x) = f^–1 (x), then the value of g' (1) If the function f (x) = x3 ex/2 and g (x) = f–1(x), then the value of g · The function f(x)=x^2 The graph of g(x) is f(x) translated to the right 3 units and down 3 units What is the function rule for g(x)?F (x)=2x3,\g (x)=x^25,\f (g (x)) f (x)=2x3,\g (x)=x^25,\f\circ \g f (x)=2x3,\g (x)=x^25,\ (f\circ \g) (2) functioncompositioncalculator f (x)=2x3, f (x3) en



Functions Algebra All Content Math Khan Academy



Solved The Graph Of A Function F Is Illustrated To The Right Use The Graph Of F As The First Step Toward Graphing Each Of The Following Functions Course Hero
· Stack Exchange network consists of 177 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack ExchangeThis is a useful technique Whichever method you use (bitbybit or allinone), the answer is ( g o f ) (1) = g ( f (1)) = – I just computed ( g o f ) (1);2801 · Ex 23, 3 A function f is defined by f(x) = 2x – 5 Write down the values of (i) f(0) (ii) f(7), (iii) f(–3), Given f(x) = 2x – 5 Putting value of x in f(x) f(0) = 2 × 0 – 5 = 0 – 5 = –5 f(7) = 2 × 7 – 5 = 14 – 5 = 9 f(−3) = 2 × (−3) – 5




Answered Nobem 13 G X 1 X 1 Fx 1 X 2 Bartleby



Answered 271 4 2 Combining Functions Composite Bartleby
How do you solve lo g 3 ( 5 x 2 ) = 3 ?If u get 3g at 60 cents u are only getting 0053g per cent but if u get 50g at $100 u are getting 05g per cent (u get 0447g more with 50g at $100 than 3g at 60 cents) Hope this helps )325 Explain the meaning of a higherorder derivative




Solved 1 Given The Functions J T X 1 3 X Determine A Chegg Com




F X X 3 G X 2x 2 4 Find F G X Brainly Com
F f in two ways f ( x 1) f ( x 1) is a change on the inside of the function, giving a horizontal shift left by 1, and the subtraction by 3 in f ( x 1) − 3 f ( x 1) − 3 is a change to the outside of the function, giving a vertical shift down by 3 The transformation of the graph is illustrated in Figure 9Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with stepbystep explanations, just like a math tutor322 Graph a derivative function from the graph of a given function;




What Is F G X F X X 2 36 G X X 3 2x 2 10 Enter Your Answer In The Box Brainly Com




Evaluate The Function For F X X 3 And G X X2 2 F G T 5 Brainly Com
G*(x)(3*f*(x))=0 Step 1 Pulling out like terms 11 Pull out like factors gx 3xf = x • (g 3f) Equation at the end of step 1 Step 2 Theory Roots of a product 21 A product of several terms equals zero When a product of two or more terms equals323 State the connection between derivatives and continuity;Or therefore, the function g(x) = Since, this g(x) is an exponential function it is of the form of where a is the initial value On comparing we get ;



Solved Composition Of Functions Let F X 2x 1 Gx 3x An Chegg Com




Evaluate The Function For The Given Value Of X F X Chegg Com
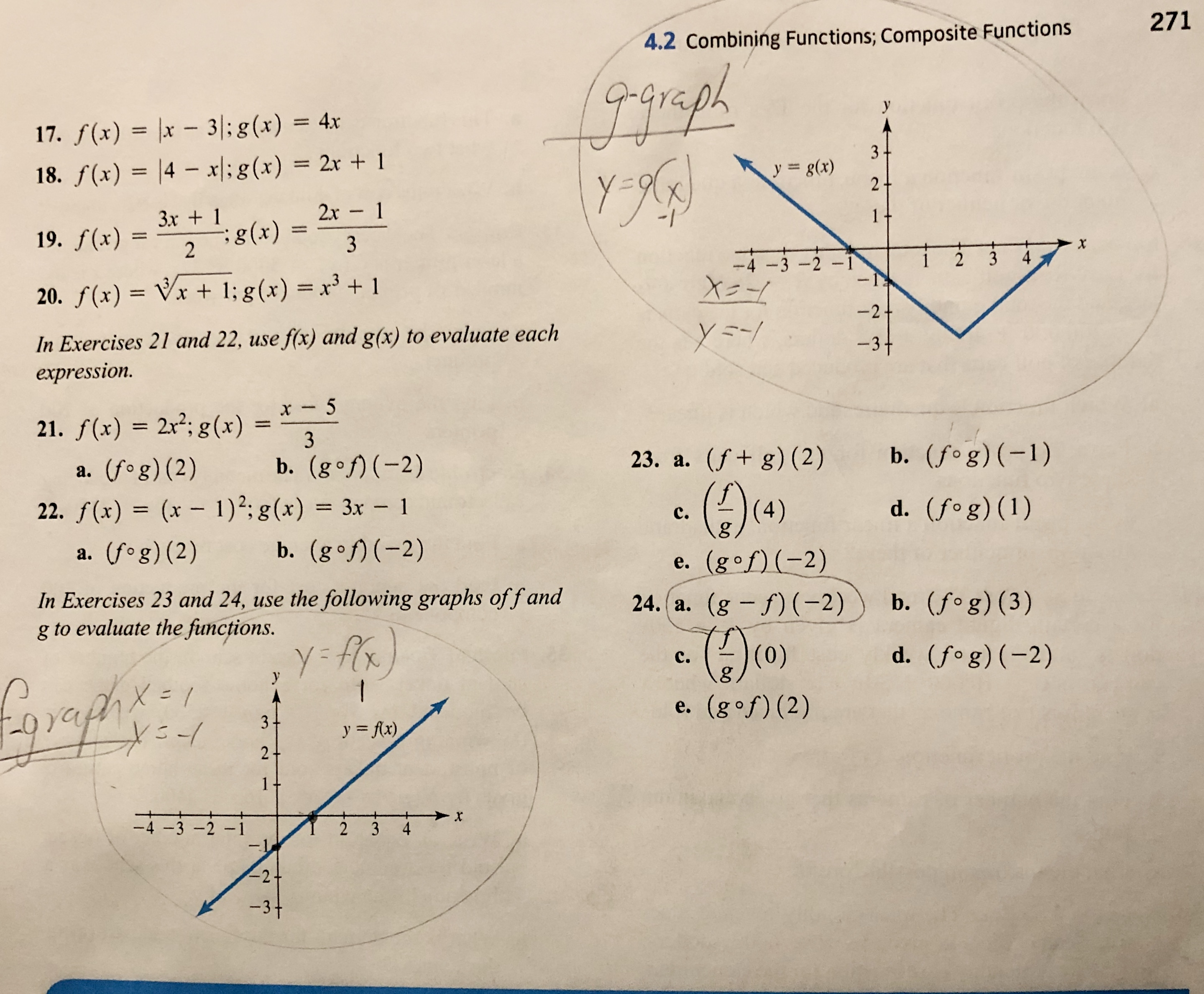
Problem 1 If f(x) = x 2 – 4x 2 and g(x) = 3x – 7, find (f o g)(x) Problem 2 If g(x) = –6x 5 and h(x) = –9x – 11, find (g o h)(x) Problem 3 If f(x) = 2x 5 and g(x) = 5x 2 – 3, find (g o f)(x) Problem 4 If f(x) = –2x 9 and g(x) = –4x 2By signing up, you'll get thousands of stepbystep solutions to your homework2801 · Ex 13, 1 Deleted for CBSE Board 21 Exams only Ex 13, 2 Deleted for CBSE Board 21 Exams only Ex 13, 3 Important Deleted for CBSE Board 21 Exams only You are




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com




Let F X X 2 4x 3 X Gt 2 And Let G Be The Inverse Of F Find The Value Of G Where F Youtube
Learning Objectives 321 Define the derivative function of a given function;Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, historyFg(5) means substitute 5 for x in the right side of g(x), simplify, then substitute what you get for x in the right side of f(x), then simplify It's a "double substitution" To find fg(5), work it from the inside out In fg(5), do only the inside part first




Help Me If F X X 2 1 And G X 2x 3 What Is The Domain If F G X Brainly Com




Use The Graph That Shows The Solution F X G X F X X 2 4x 2 G X 1 2 2 1 What Is The Brainly Com
G(x)= x2 1 x (8) f(x) = 3x 4 (9) f( ) = 3( ) 4 (10) f(g(x)) = 3(g(x)) 4 (11) f(x2 1 x) = 3(x2 1 x) 4 (12) f(x 2 1 x) = 3x 3 x 4 (13) Thus, (f g)(x) = f(g(x)) = 3x2 3 x 4 Let's try one more composition but this time with 3 functions It'll be exactly the same but with one extra step Find (f g h)(x) given f, g, and hThe initial value of g(x) is 2Free functions range calculator find functions range stepbystep




If F X X 2 2 And G X 4f X 1 Then Which Of The Following Is The Value Of G 3 Wyzant Ask An Expert




If F X 3x 2 And G X X 2 Then Fog X
F (x)=x^4−x^29 g (x)=x^33x^212 f g = x^4 x^2 9 x^3 3x^2 12 = x^4 x^3 x^2 3x^2 9 12 = x^4 x^3 2x^2 3 2 What is (f⋅g) (x)?Given f (x) = 3x 2 – x 4, find the simplified form of the following expression, and evaluate at h = 0 This isn't really a functionsoperations question, but something like this often arises in the functionsoperations context This looks much worse thanThe composition can also work in the other order Given f ( x) = 2 x 3 and g ( x) = – x2 5, find ( f o g ) (1)




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com




If F X X 2 And G X 2x Then Evaluate I F G 3
Using the rule of reflection across xaxis;If f(x) = 2x 3 and g(x) = (x 3)/2, what is the value of fg(5)?Replace the x in the f(x) equation with the value of g(x) to get (x3)cubed 2That's it When you write f(x) = x3 2 That means x can be any number, equation or function and whatever that value is, it goes into x3 2




Answered 1 7 2 6 H 4 X 12 6 G X 3 F X 9 3 1 Bartleby




Given That G X 3x 2 2x 1 Find Each Of The Following A G 0 B G 1 C G 3 D G X Brainly Com
· Given the function f(x)= is reflected across the xaxis to create g(x) The rule of reflection across x axis is then;G(x) = (x 2)2 k g(x) = (x 8)2 k g(x) = (x h)2 5 g(x) = (x h)2 15Simple and best practice solution for g(x)=f(1/3x) equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework If it's not what You are looking for type in the equation solver your own equation and let us solve it




If F X X 2 2 And G X 2x 2 X 3 Find F G X Brainly Com
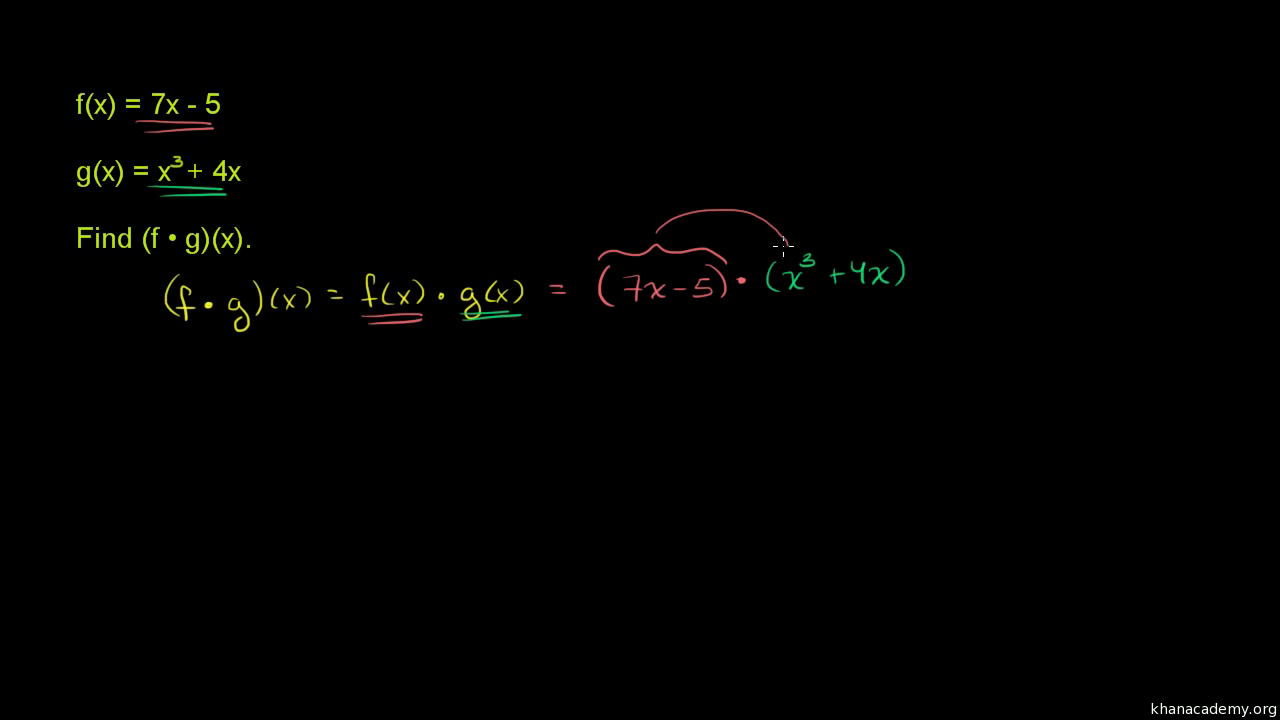



Functions Algebra All Content Math Khan Academy
Answer to If f(x) = x^2 and g(x) = x 1, what is f(g(x))?1218 · Best Answer First one (3X^2 5) (x2) = 3x^3 6x^2 5x 10 Second one is written incorrectly, I think you meant f/g (x) f (x) = 2x^25x3 = (2x1) (x3) then f/g = (2x1) (x3) / (x) (2x 1) x cannot equal 0 or 1/2 because the denominator would be ZERO Simplify to (x3)/x (the (2x1)'s 'cancel out')If f(x) = F(G(x)), then fis continuous at all points in its domain if Gis continuous at all points in its domain and Fis continuous at all points in its domain ( Note that we can repeat the process to get the same result for a function of the form F(G(H(x))) ) Example Evaluate the following limit lim x!1 r x2 x 1 x 3 Let G(x) = x2 1 x3




If F X 1 X 1 And G X X 2 X 3 Then Number Of Points




Find The Greatest Common Divisor Of F X 2x 3 2x 2 X 4 And G X X 4 3x 3 4x 2 3x Mathematics Stack Exchange
F(x)= 3x^2 1 g(x)= x 2 Now , f(g(x)) means a composition of the two functions which have the Domain of the function "g" , but it's range is of "f" It is written as "f o g" ( f compose g) And it's very easy to find the value f(g(x)) = f(x2) = 3(x2)^2 1 = 3(x^2 4x 4) 1 = 3x^2 12x 11 · Replace all x's in g(x) with the function f(x) to get g( f(x) ) = ( x3 )^2 g(f(x)) means that you replace all x's in g(x) with the function f(x) The easiest way to do this is rewrite g(x), replacing all x's with a blank set of parenthesis, like this g( f(x) ) = ( )^2 Now place the function f(x) into the parenthesis g( f(x) ) = ( x3 )^2Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history




Find The Maximum Value Of The Function F X 2x 2 Chegg Com




The Graph Of F X 3 2 X 3 Is Shown Below G X Is A Transformation Of F X How Would You Write The Brainly Com
Solution Steps g ( x ) = f ( x 2 ) 2 g ( x) = − f ( x 2) 2 Use the distributive property to multiply f by x2 Use the distributive property to multiply − f by x 2 \left (f\right)x2\left (f\right)2 ( − f) x 2 ( − f) 2 Multiply 2 and 1 to get 2 Multiply 2 and − 1 to get − 2Get an answer for 'If f(x)= 2/(x3) and g(x)= 1/x then what is (gof)(x)?' and find homework help for other Math questions at eNotesGraph g (x)= (x3) g(x) = (x − 3) g ( x) = ( x 3) Rewrite the function as an equation y = x− 3 y = x 3 Remove parentheses y = x− 3 y = x 3 Use the slopeintercept form to find the slope and yintercept Tap for more steps The slopeintercept form is y = m x b y = m x b, where m m is the slope and b b is the yintercept
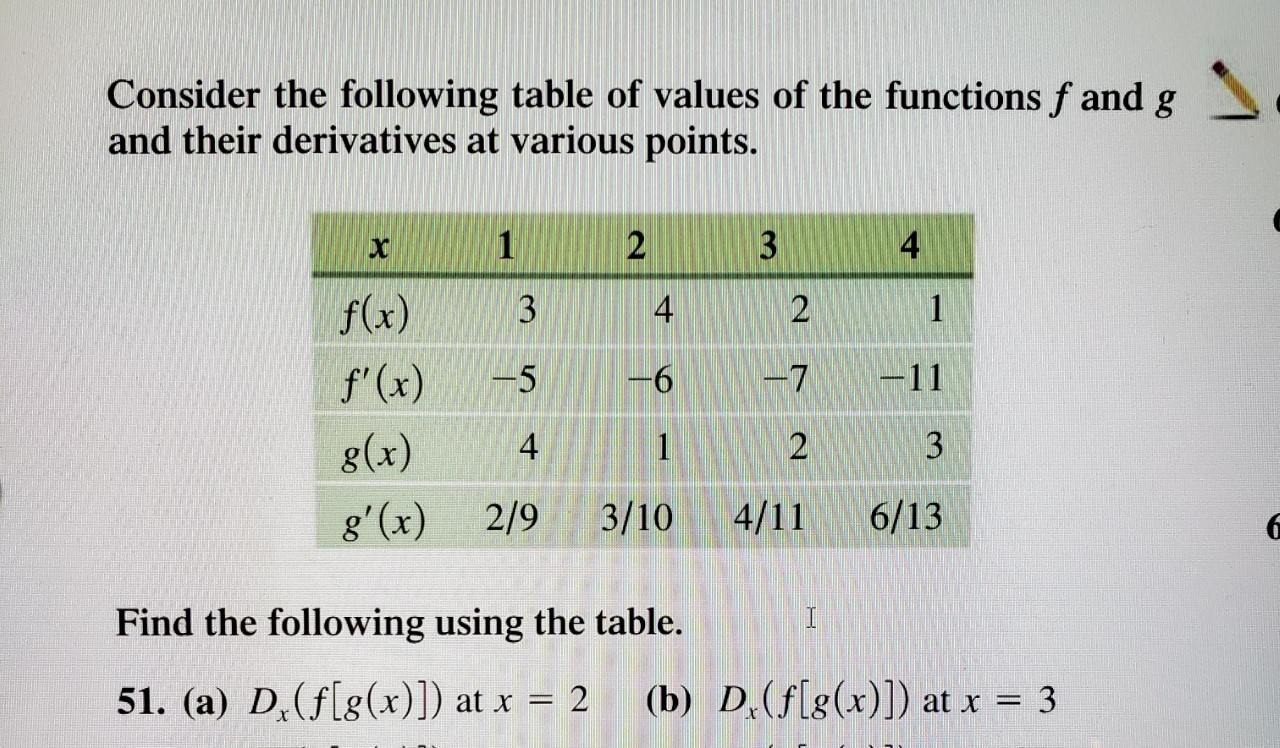



Answered Consider The Following Table Of Values Bartleby
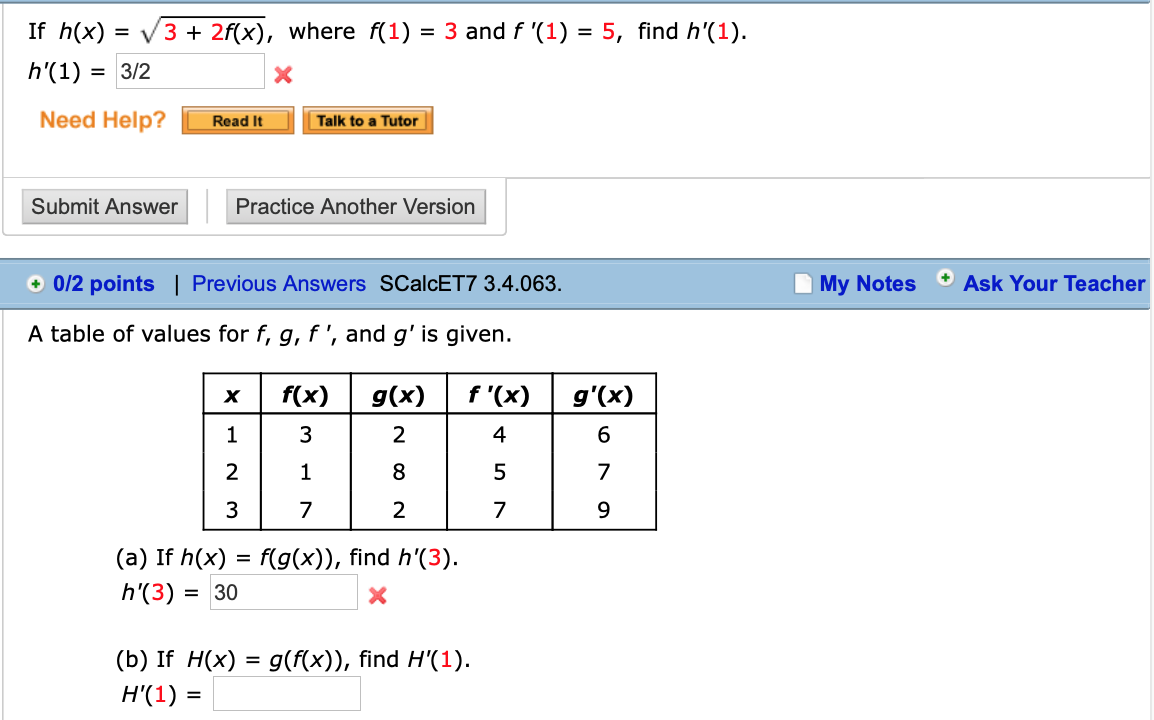



Q1 If H X 3 2f X Where F 1 3 Chegg Com
Then, f(x)g(x) = 4x 2 4x 1 = 1 Thus deg( f ⋅ g ) = 0 which is not greater than the degrees of f and g (which each had degree 1) Since the norm function is not defined for the zero element of the ring, we consider the degree of the polynomial f ( x ) = 0 to also be undefined so that it follows the rules of a norm in a Euclidean domain · F(x) = 3x^2 1 g(x) = 1 x (f g)(x) = 3x^2 1 (1 x) = 3x^2 1 1 x = 3x^2 x (f g)(2) = 3(2)^2 2 = 3(4) 2 = 12 2 = 14Example 3 Given f ( x ) = x2 1 and g ( x ) = x – 4 , find ( f g ) ( x ) and ( f g ) ( 3 ) Solution Step 1 Solve for ( f g ) ( x ) Since ( f g ) ( x ) = f
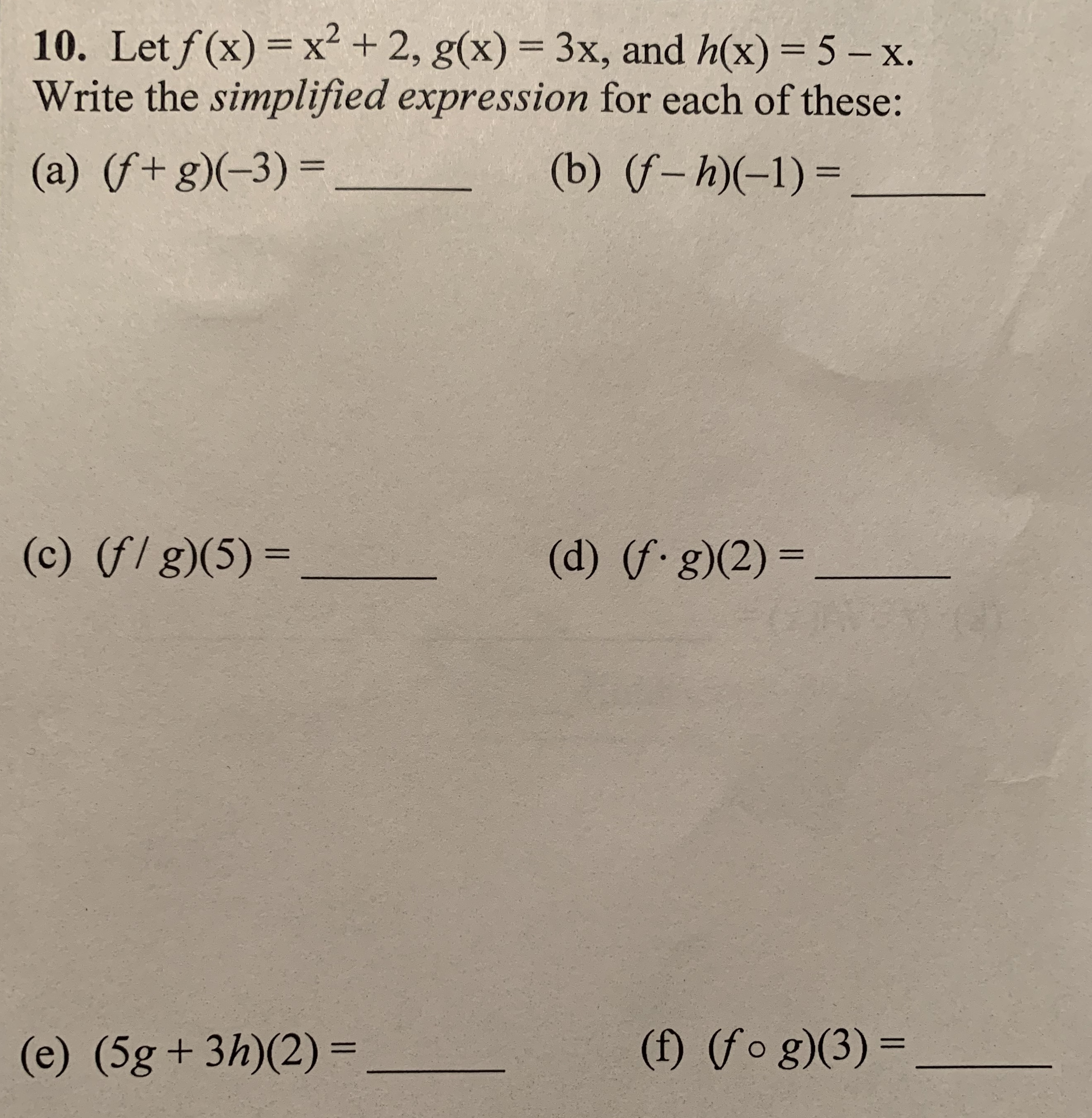



Answered 10 Let F X X 2 G X 3x And Bartleby




Operations With Functions Ppt Download
· What must be added to x^4 2x^3 2x^2 x 1 so that the resulting polynomial is exactly divisible by x^2 2x 3 asked Apr 8 in Algebraic Expressions by Madhuwant ( 381k points) division of algebraic expressions
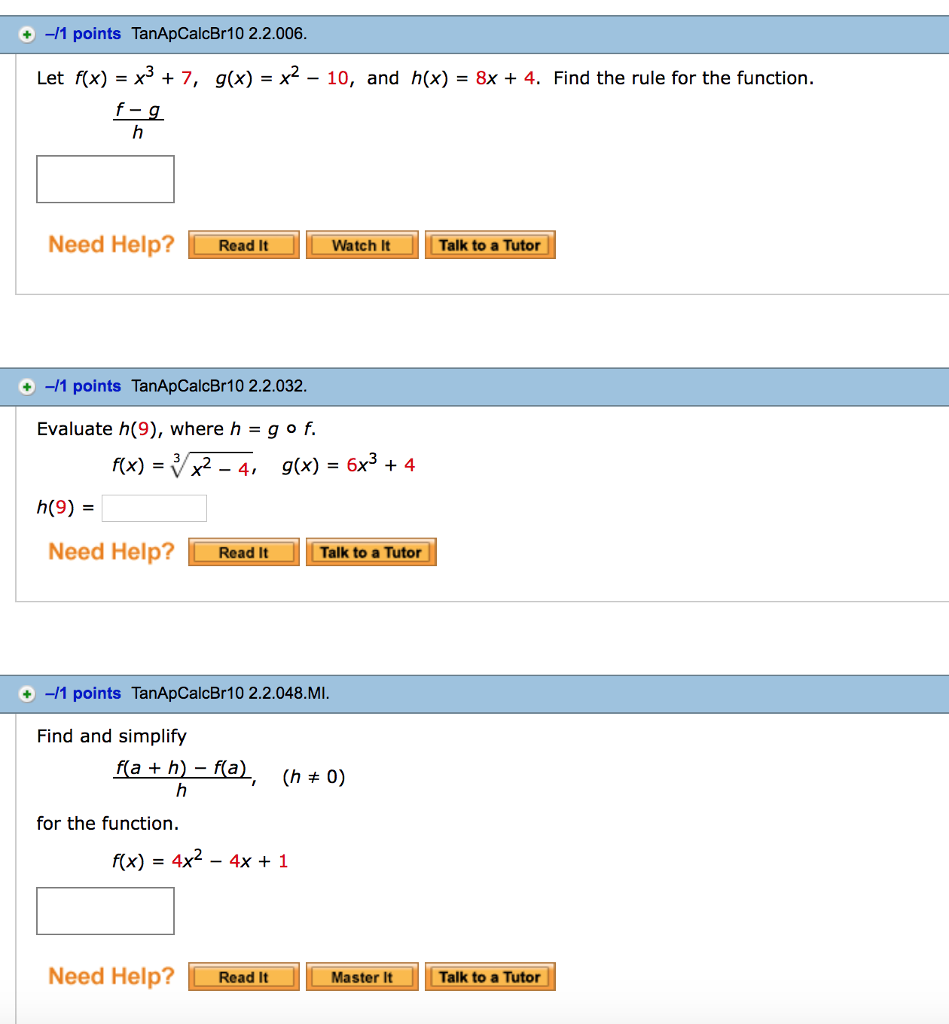



1 Points Tanapcalcbr10 2 2 006 Let F X X3 7 Chegg Com
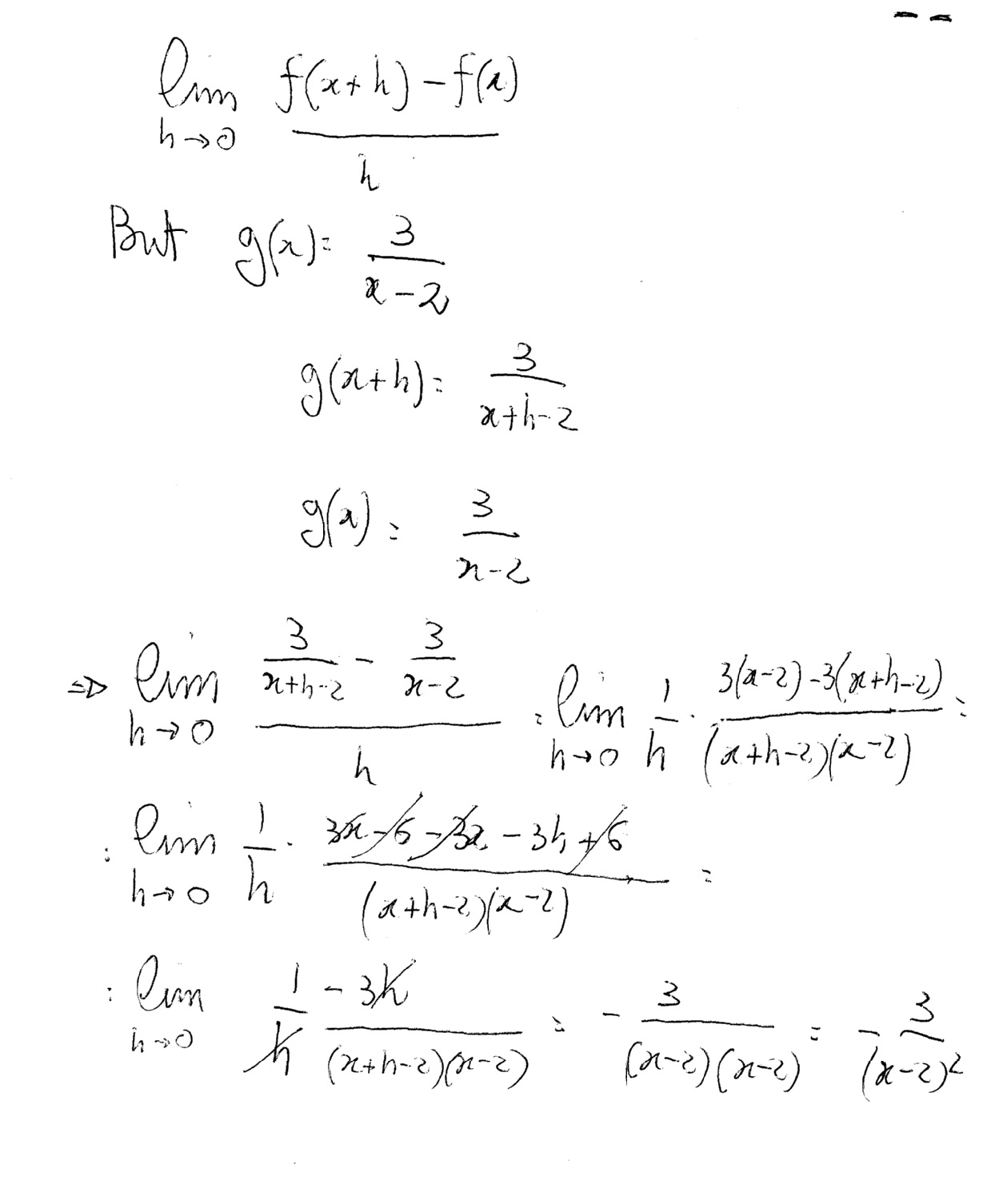



How To Find The Derivative Function Of G X 3 X 2 F X F X H F X H Socratic



F X 2x 3 5x 2 G X 2x 1 Find F G X Youtube
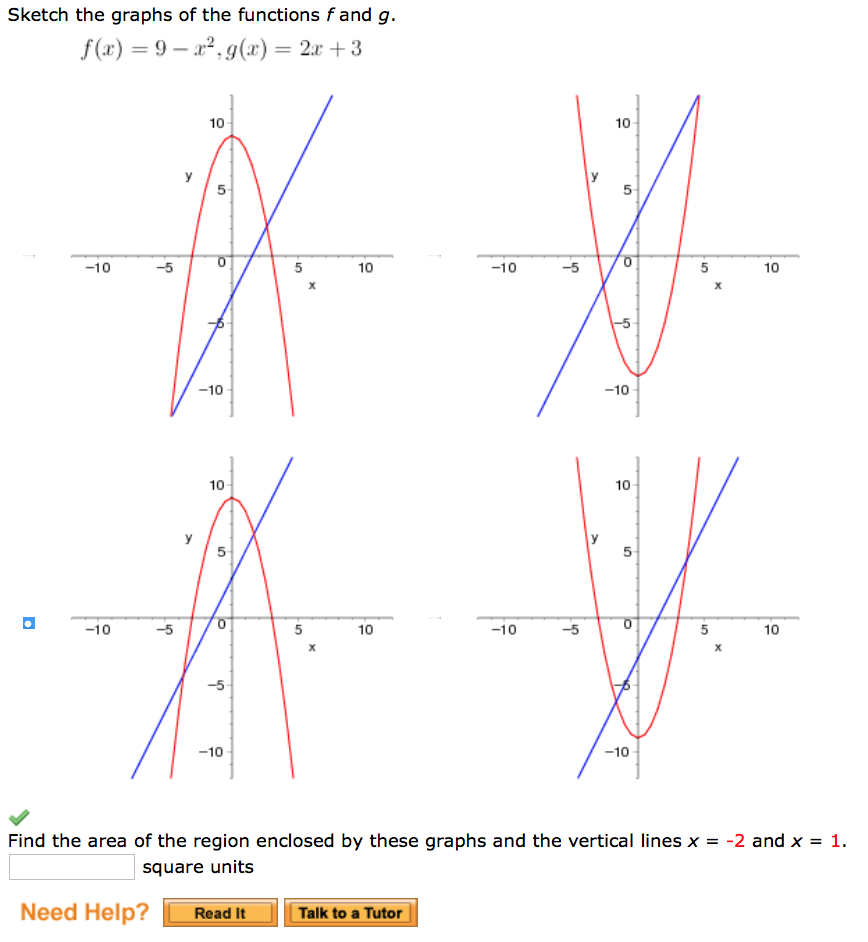



Sketch The Graphs Of The Functions F And G F X 9 Chegg Com




Use The Graph That Shows The Solution F X G X F X 3 4x 2 3x 1 G X 2 X What Is The Brainly Com
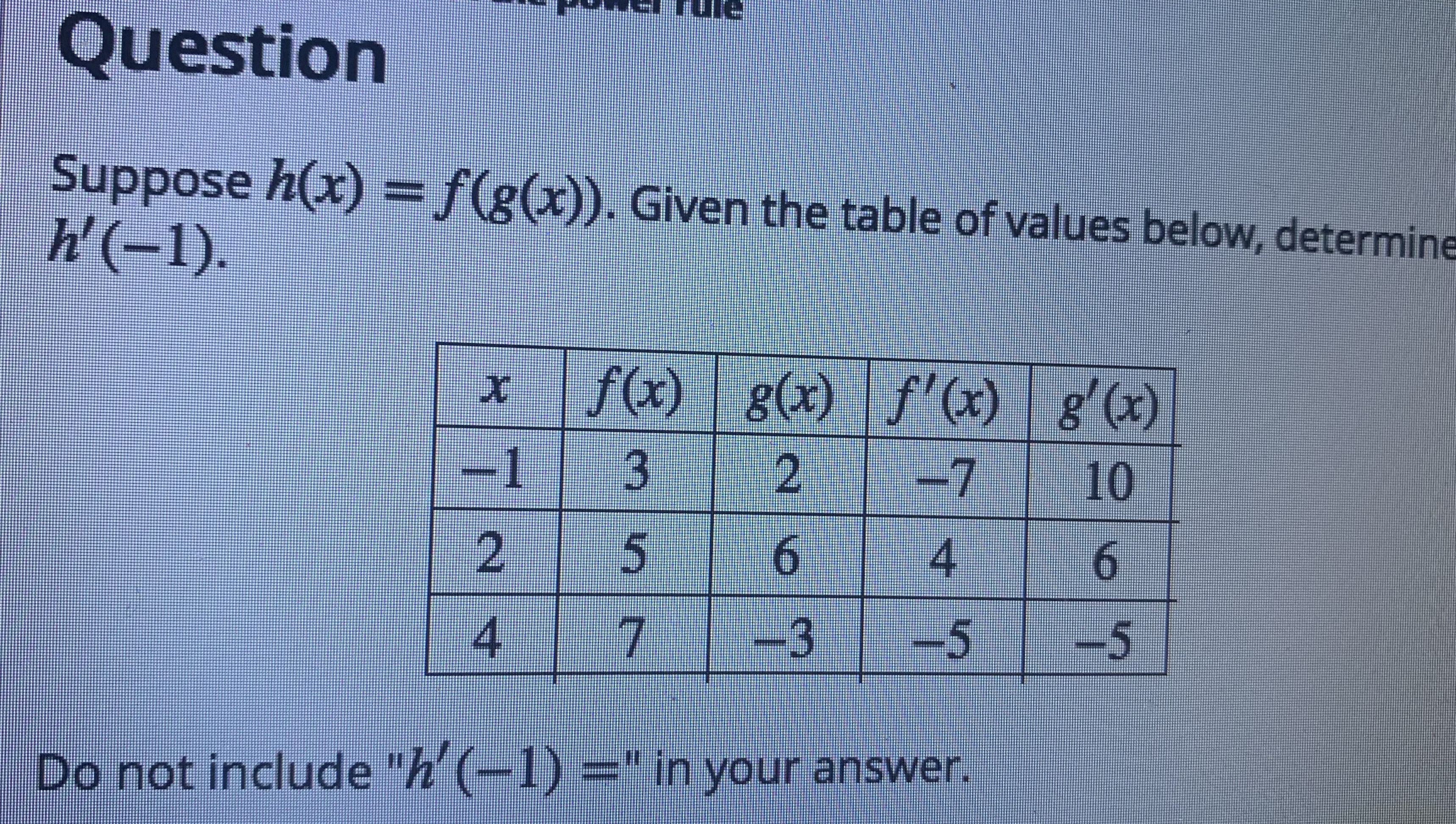



Answered Question Suppose H X F G X Given Bartleby
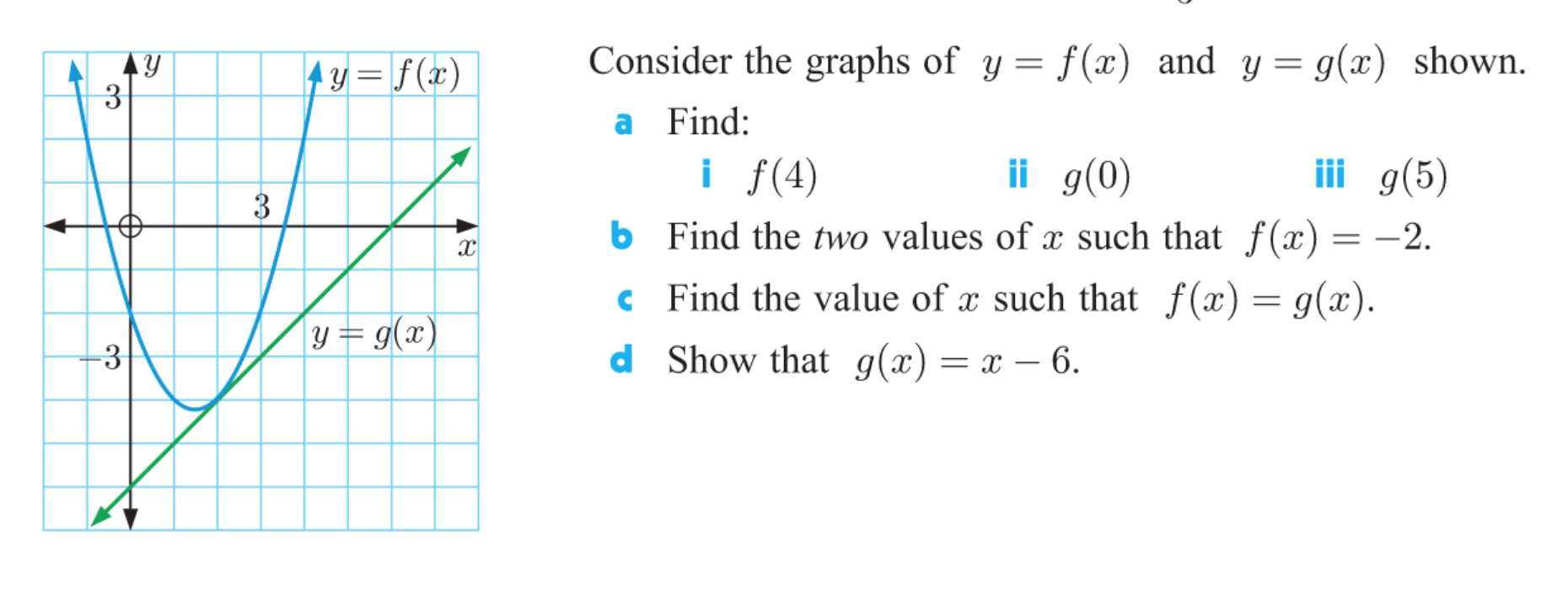



Answered Consider The Graphs Of Y F X And Y Bartleby




Domains 31 F X X3 2x2 G X 3x2 1 32 F X Chegg Com




Answered The Functions F G And H Are Defined Bartleby




If F X 3 X 2 G X 2 X 1 F G X Brainly Com



Composing Functions At A Point Expii




Verifying Inverse Functions By Composition Not Inverse Video Khan Academy
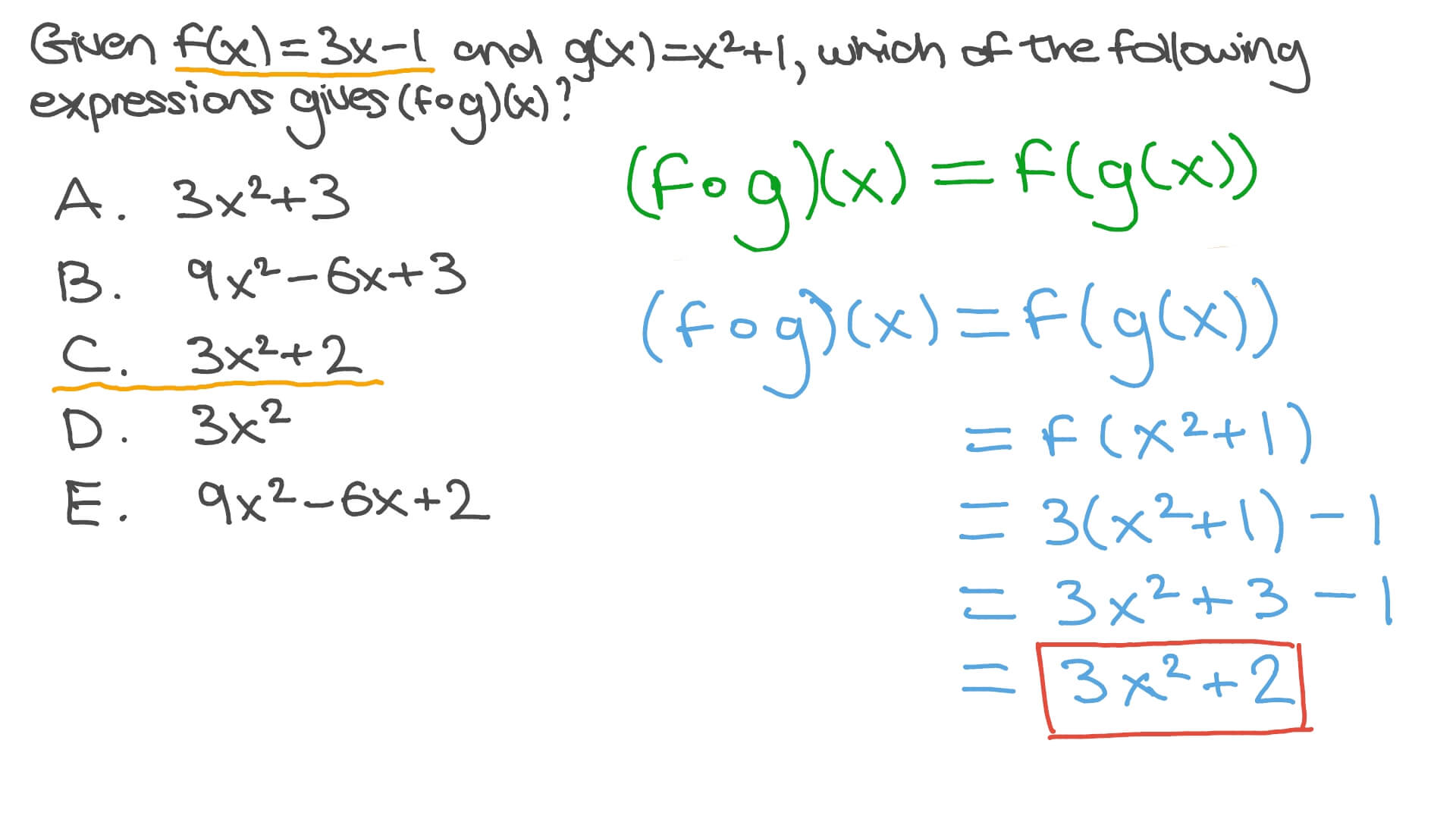



Question Video Finding The Composite Of Two Functions Nagwa




If F X X 2 And G X 2x 3 Then The Value Of Gof 1
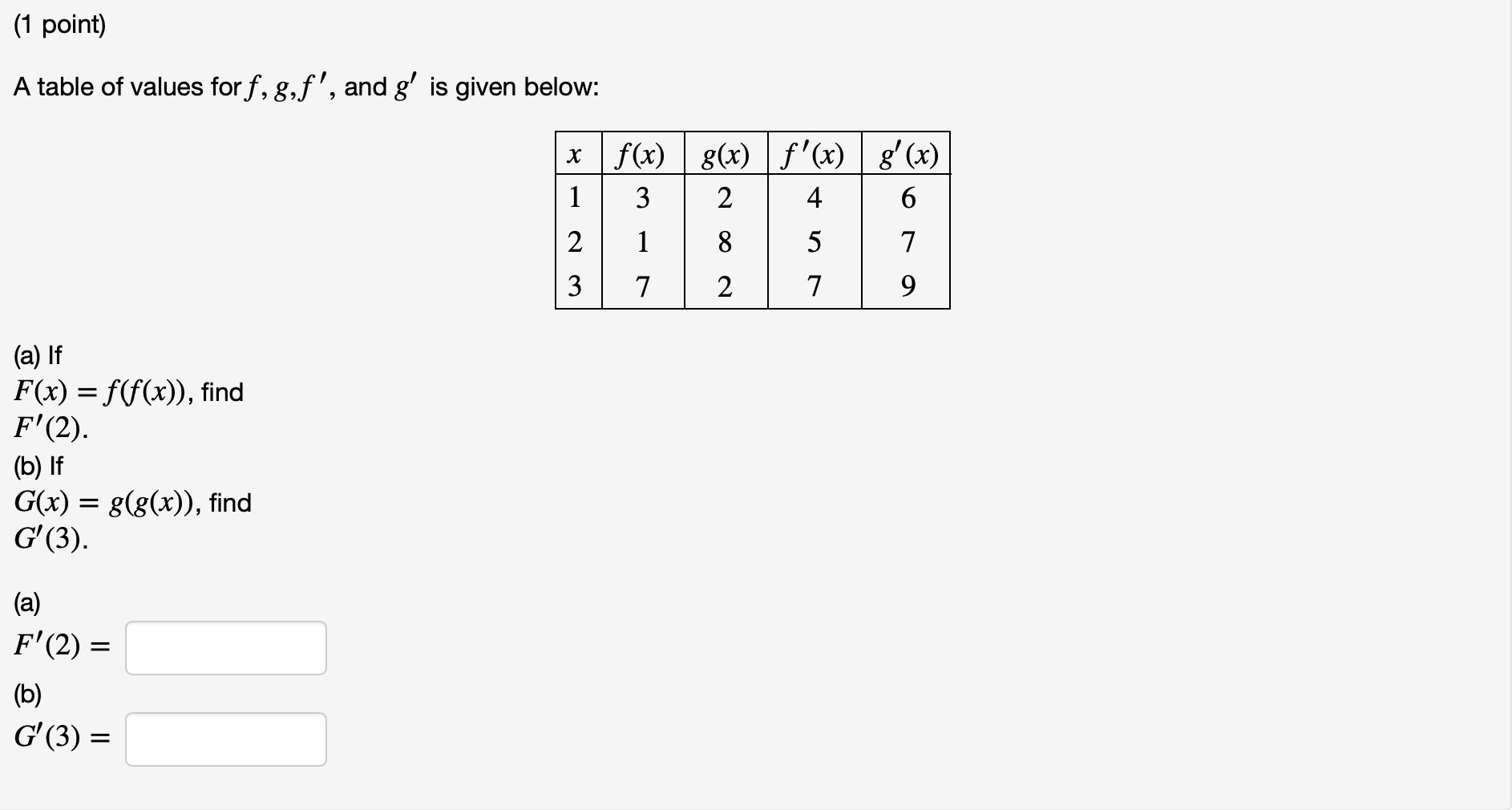



1 Point A Table Of Values For F G F And G Is Chegg Com




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com




Solved F X Then Use Transformations Of This Graph T Chegg Com
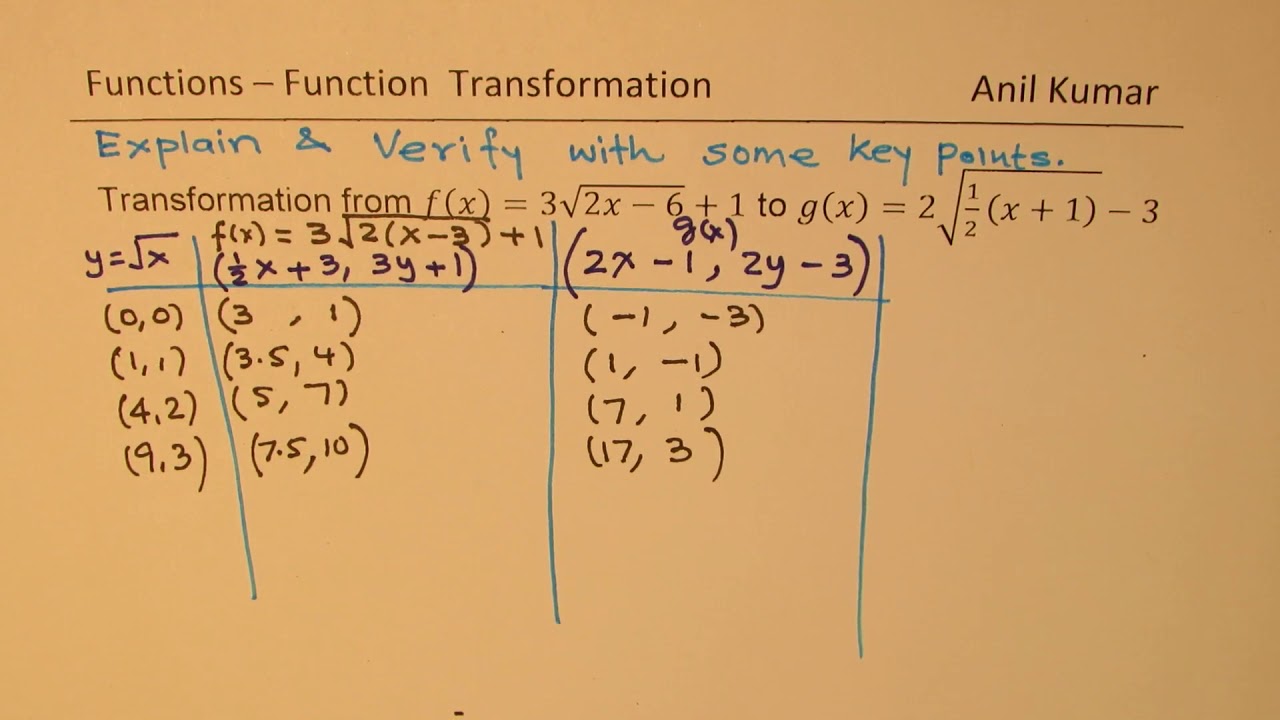



G X 2 1 2 X 1 3 Verify Transformation Of Key Points Between Functions Youtube




If F X Sqrt X 2 1 G X X 1 X 2 1 And H X 2x 3 The




Misc 1 F X X2 0 X 3 3x G X X2 0 X 2 3x




Please Help For All Values Of X F X X 1 And G X 2x 2 3 Solve Fg X Gf X Brainly Com




Misc 7 Let F X X 1 G X 2x 3 Find F G F G F G
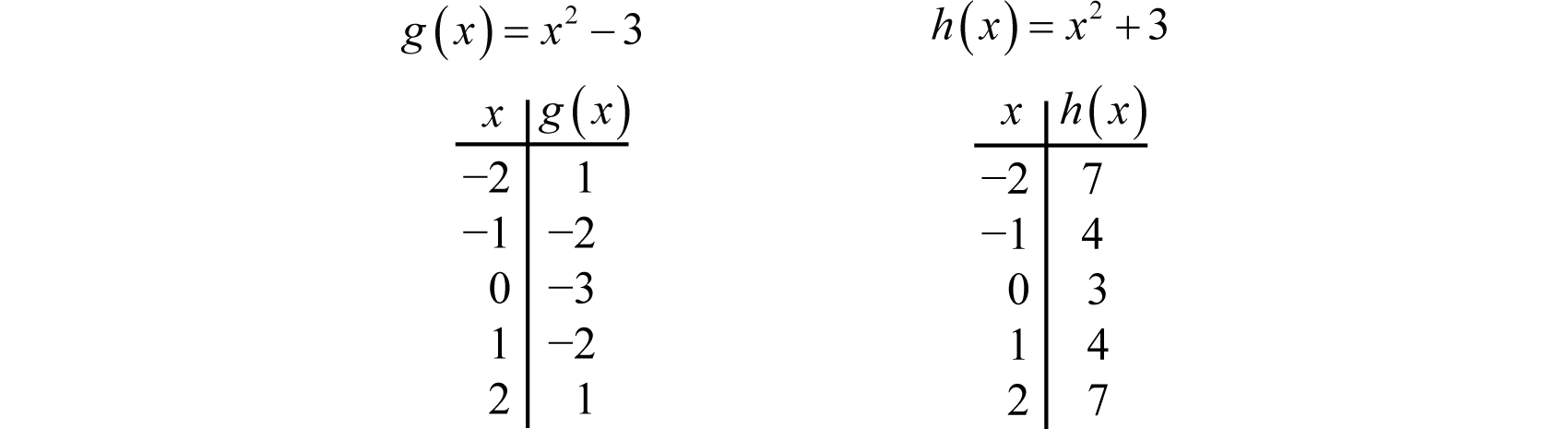



Using Transformations To Graph Functions




1 Given The Functions F X X 1 And G X 3 X Chegg Com



Let F X X 3 3x 2 And G X Be The Inverse Of It Find The Area Bounded By G X X Axis Youtube




If F X X 2 And G X 3x Then Find Gof X X 1 2 3




G X 2 F X 2 Zonealarm Results
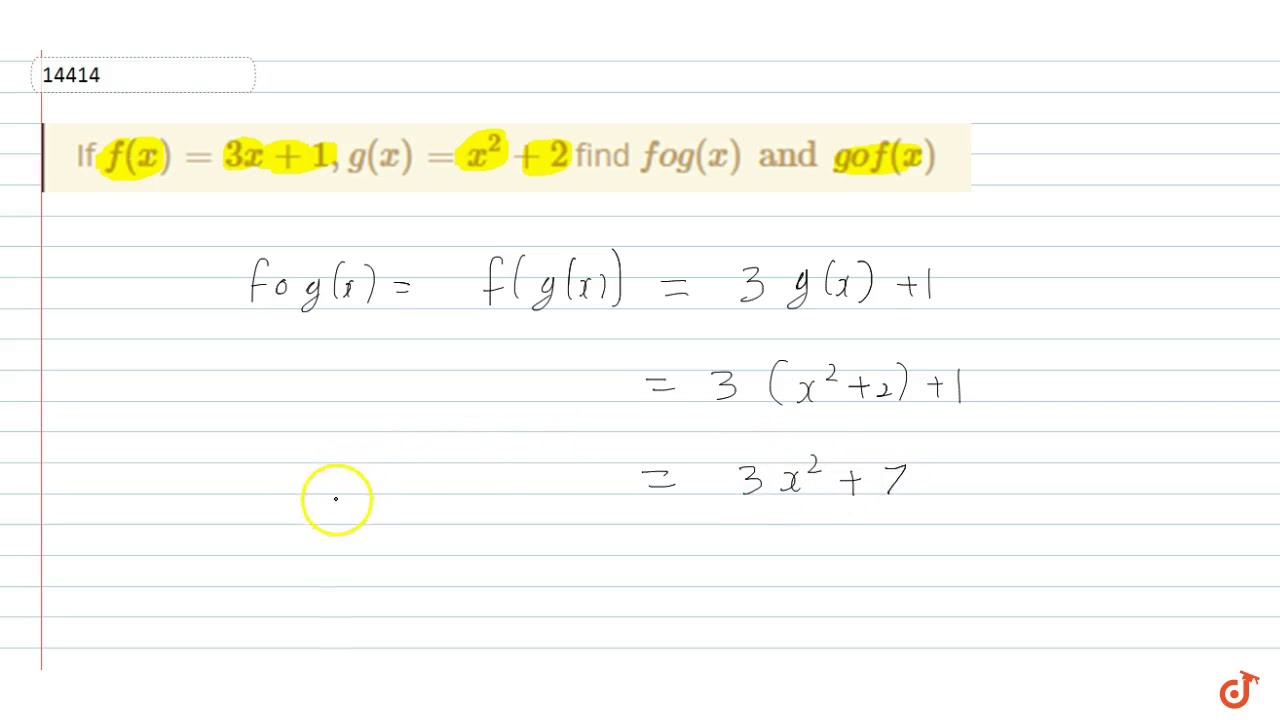



If F X 3x 1 G X X 2 2 Find Fog X And Gof X Youtube




If F X X 2 1 And G X 2x 3 Then G O F




If F X 2x 3 G X X 3 5 Then Find Fog And Show That Fog Is
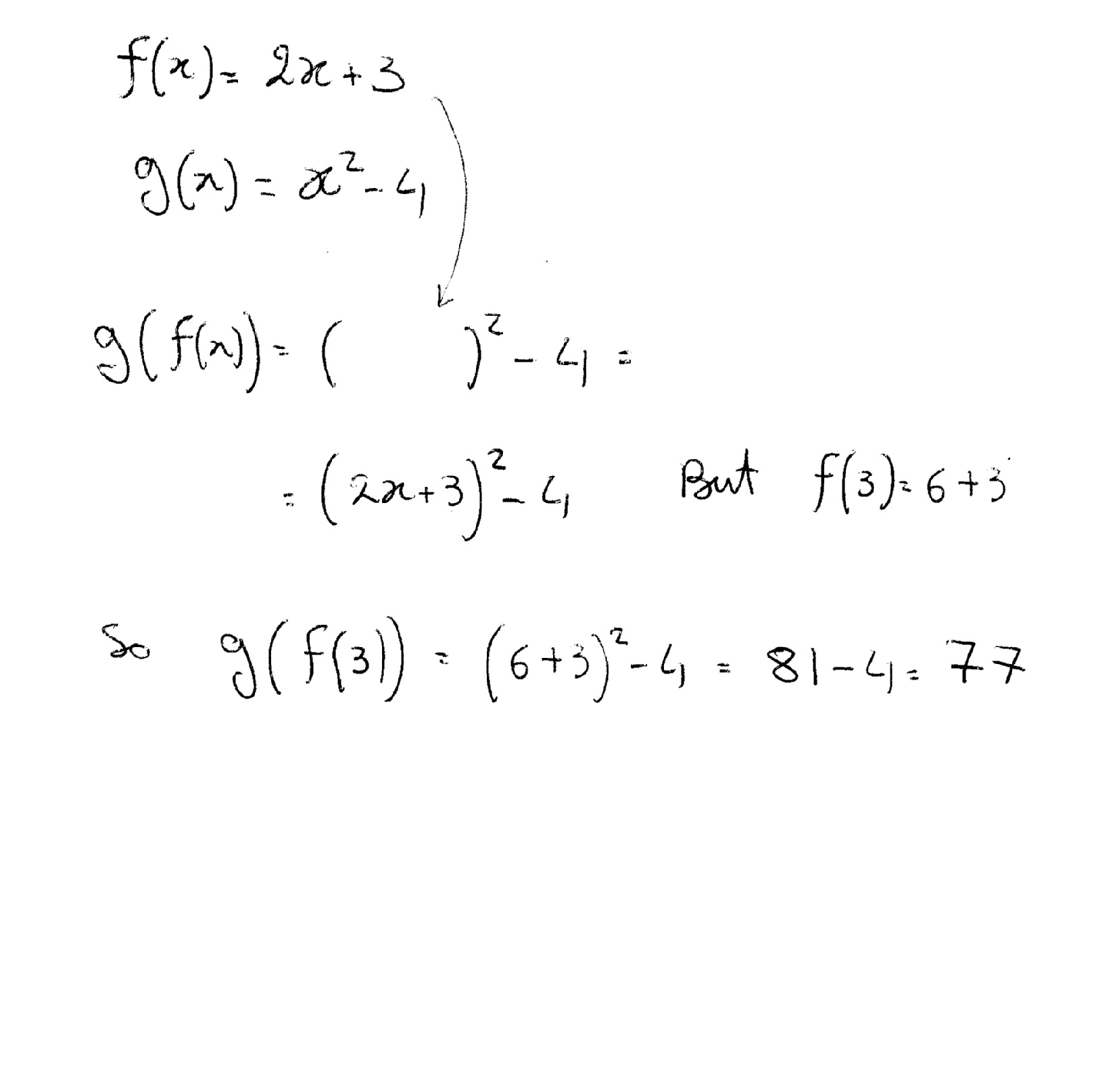



Let F X 2x 3 And G X X 2 4 And H X X 3 2 How Do You Find G F 3 Socratic




اسئلة محلولة عن الدوال والنهايات




Find 1 Gof And 2 Fog Where F X X 2 G X X 2 3x 1 Youtube




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com




Find F G X If X X 2 3 And G X 4x 2 X 4 Brainly Com




F X 9x 3 3x 2 X 5 G X X 2 3
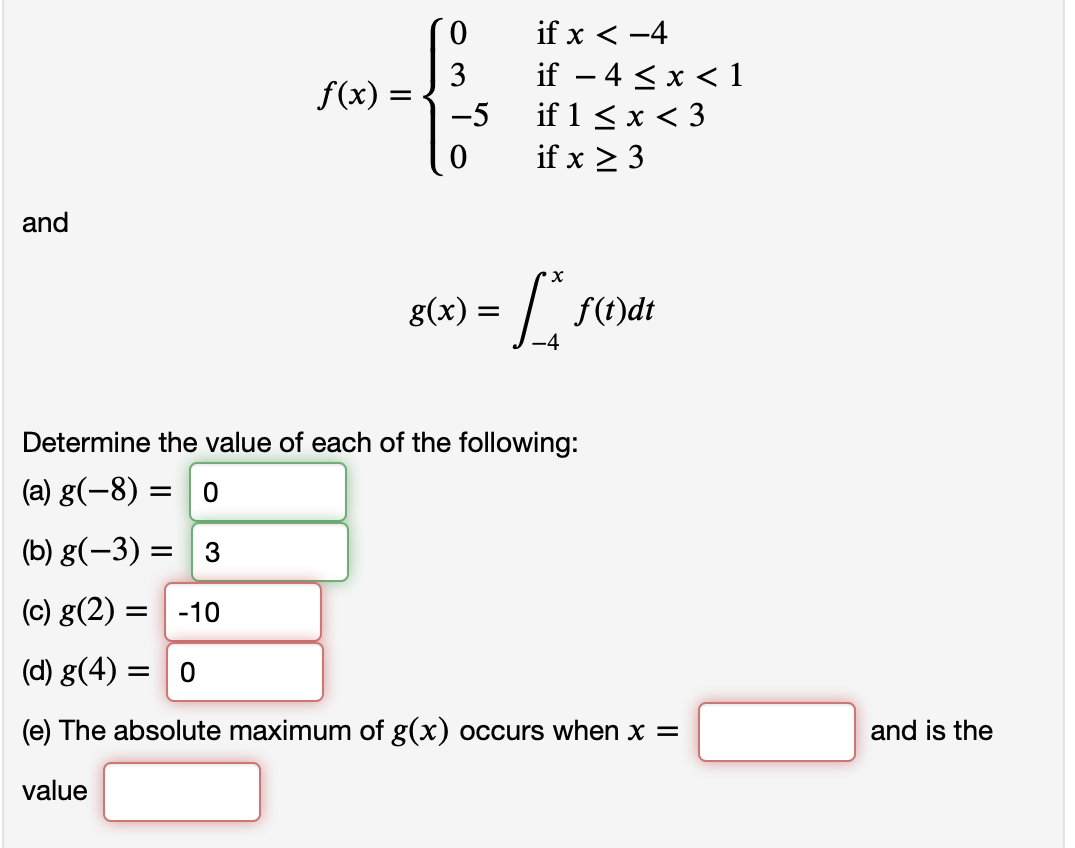



Let 𝑓 𝑥 03 50 If 𝑥 Lt 4 If 4 𝑥 Lt 1 If Chegg Com




F N R Such That F X 2x 1 2 And G Q R Such That G X



Are Inverses F X




If F X And G X Are Two Functions With G X X 1 X And F G X
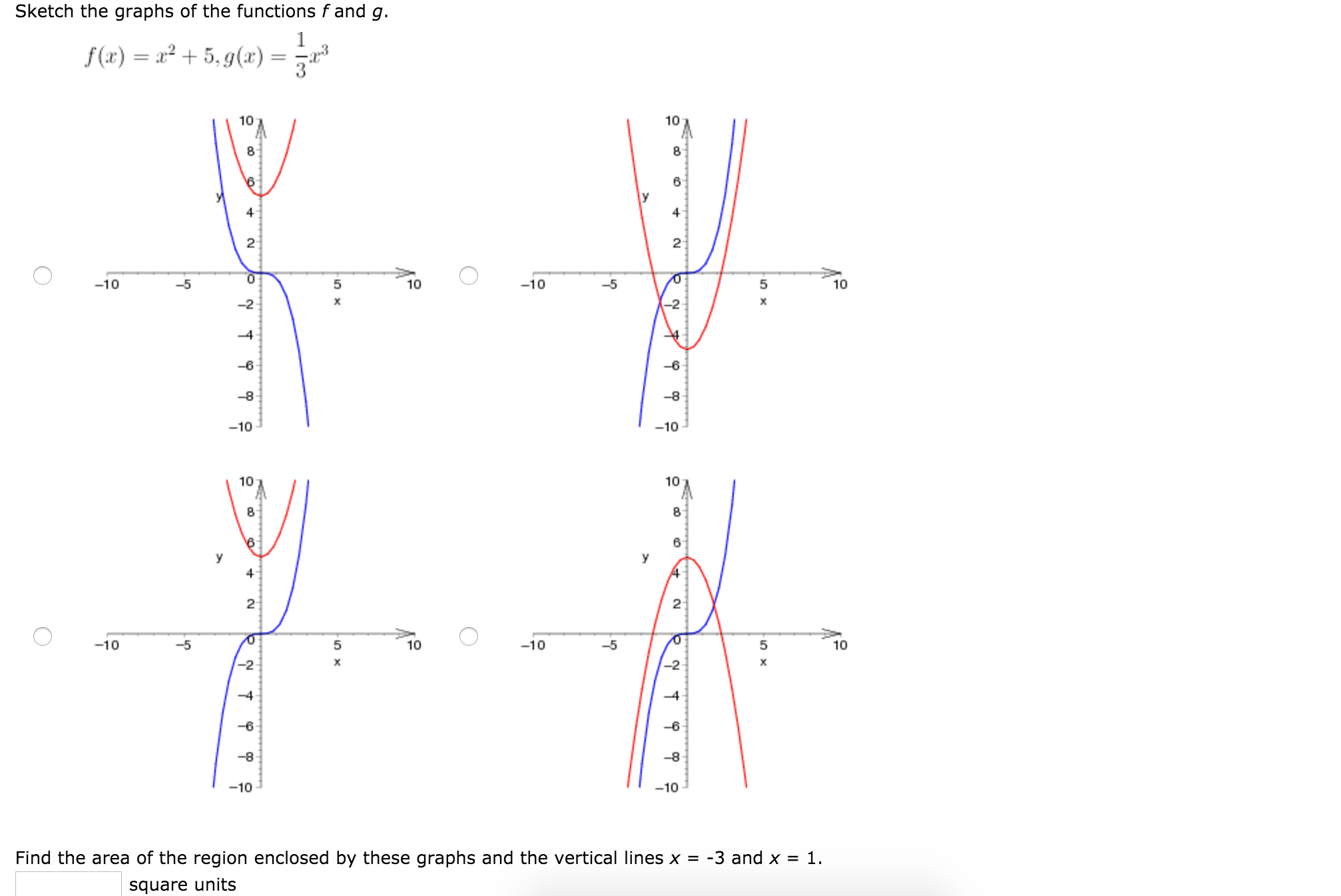



Solved Sketch The Graphs Of The Functions F And G F X Chegg Com




F X X2 What Is G X F X G X 2 2 15 Brainly Com




Answered Express The Function In The Form F G 1 Bartleby
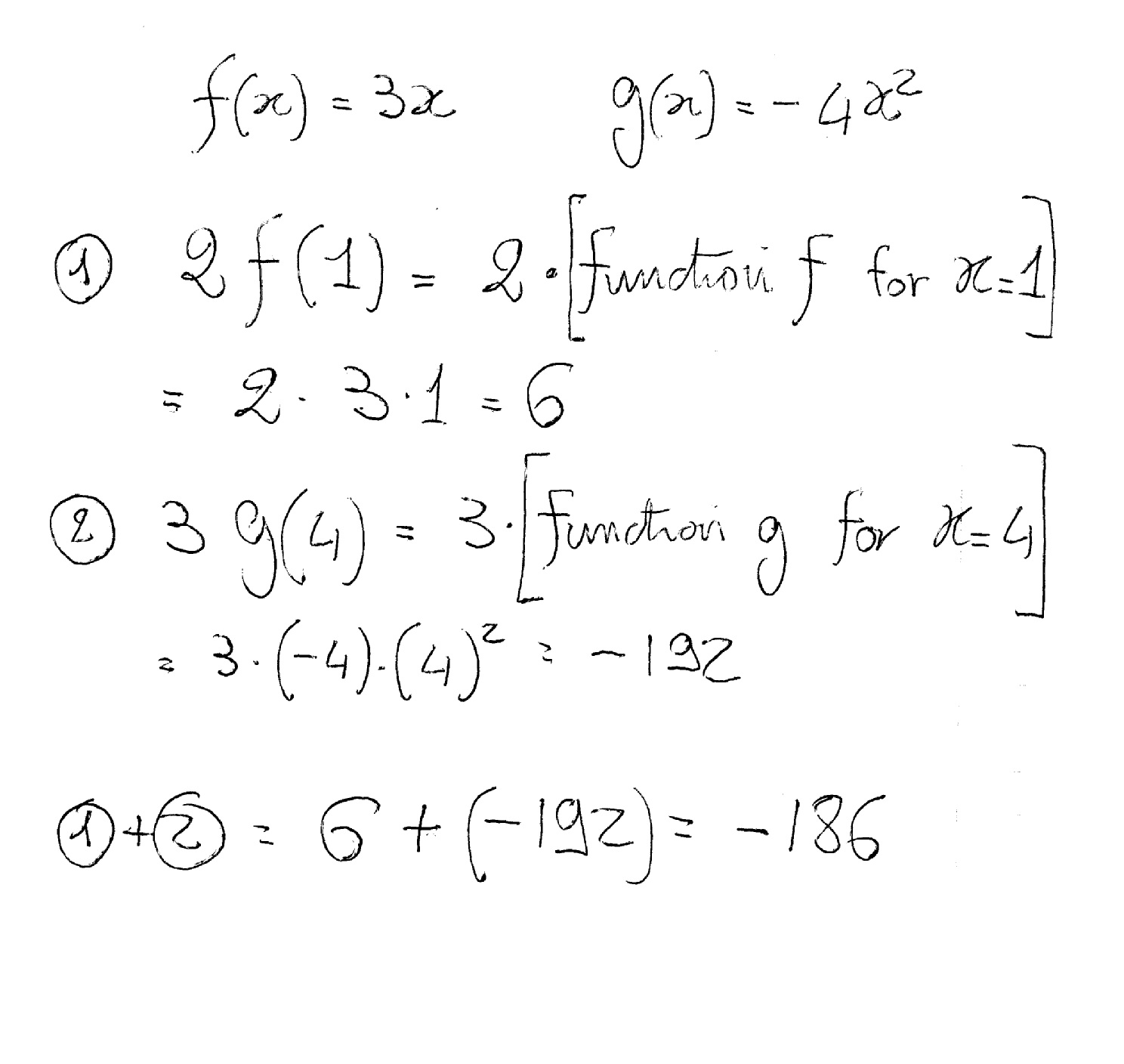



How Do Find The Value Of 2f 1 3g 4 If F X 3x And G X 4x 2 Socratic




If F G Rvecr Are Defined Respectively By F X X 2 3x 1 G X 2x
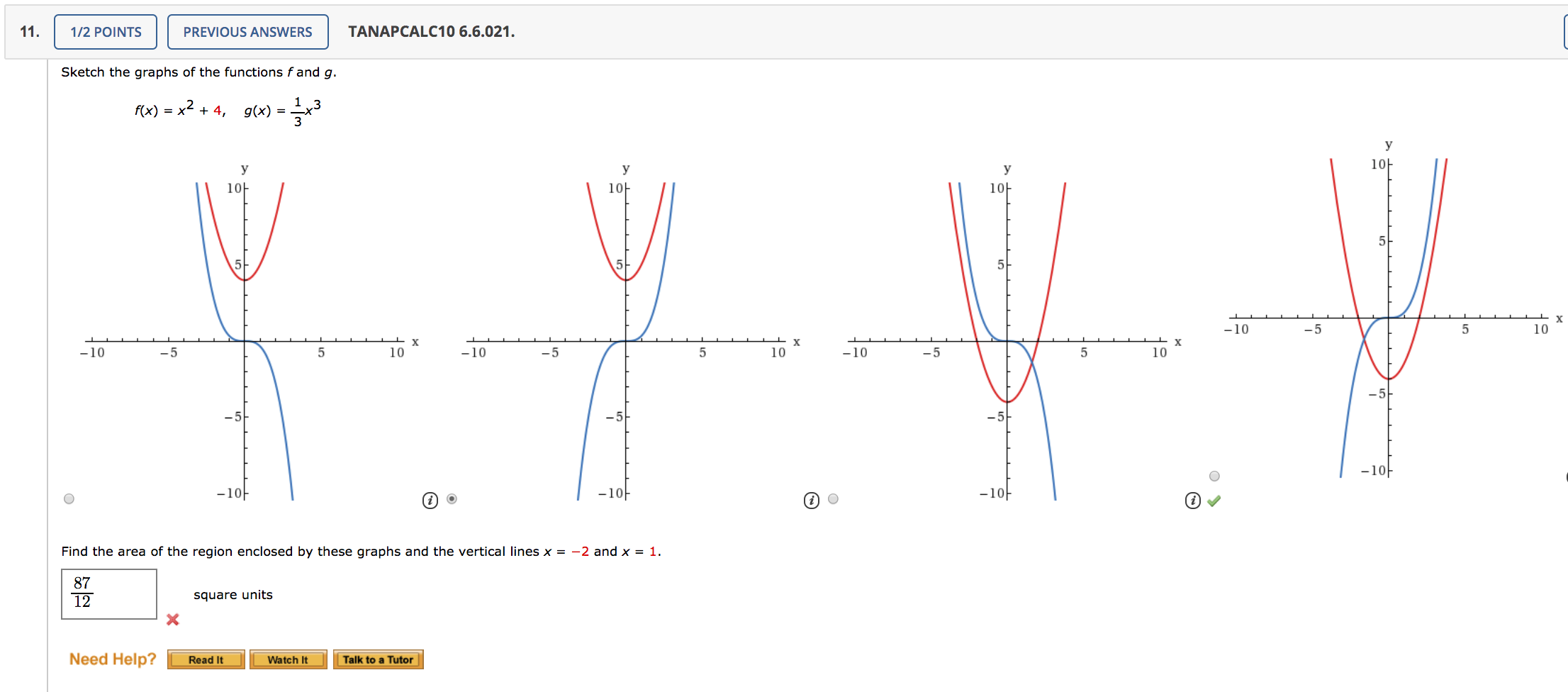



Solved Sketch The Graphs Of The Functions F And G F X Chegg Com



What Is A Function Transformation Expii




Please Help Me F X X2 What Is G X Brainly Com




Given That F X 2 X 4 And G X 3 X 5 Find Gf 3 With Noob Like Steps Please I Need A Really Clear Working To Fully Understand Thanks 3 Socratic




If F X 5 4 And G X 3 2 Find F G X Brainly Com




Solved If F X X And G X 1 Then F G X What Is Chegg Com




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com
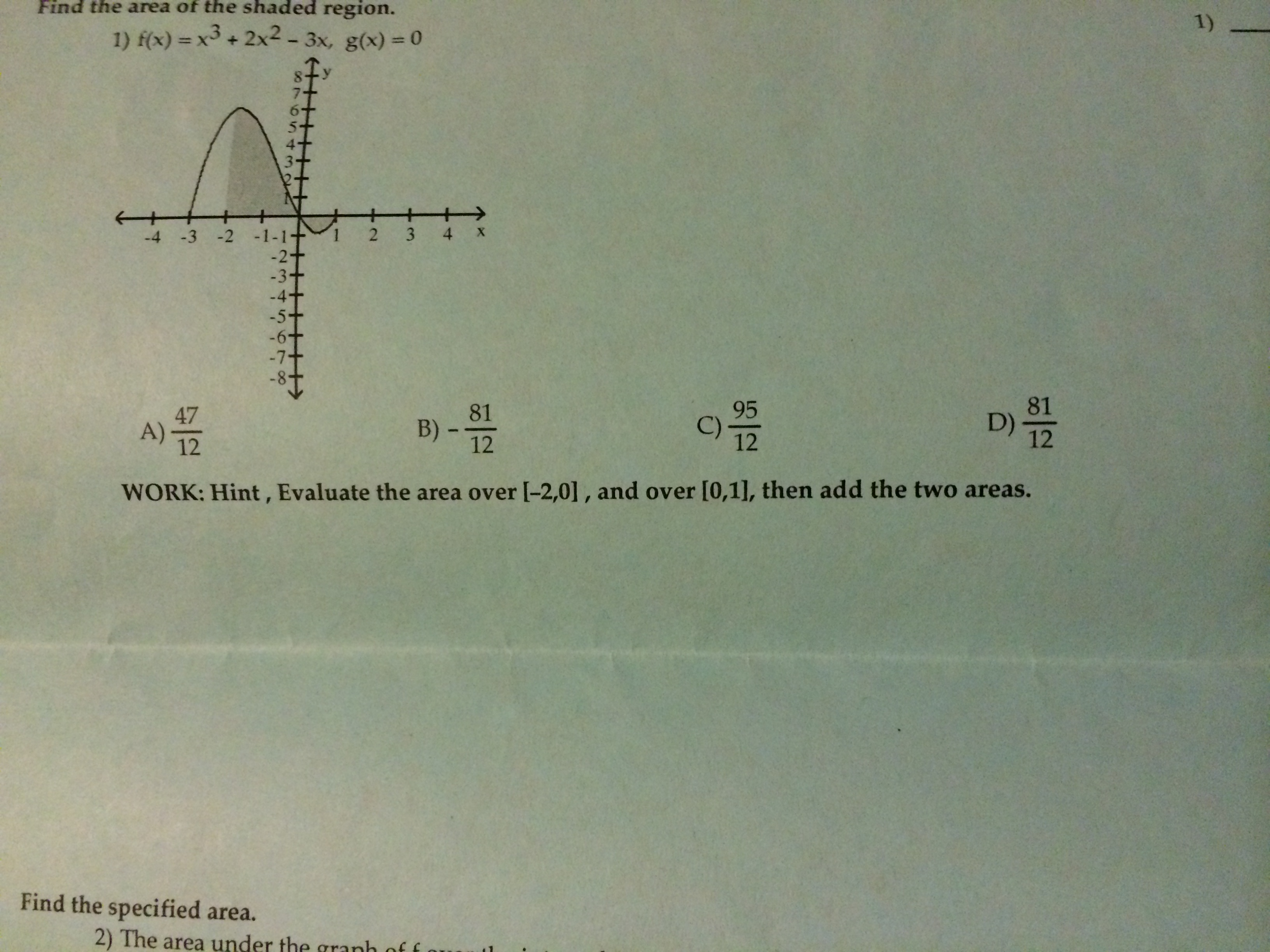



Solved Find The Area Of The Shaded Region 1 F X X 3 Chegg Com
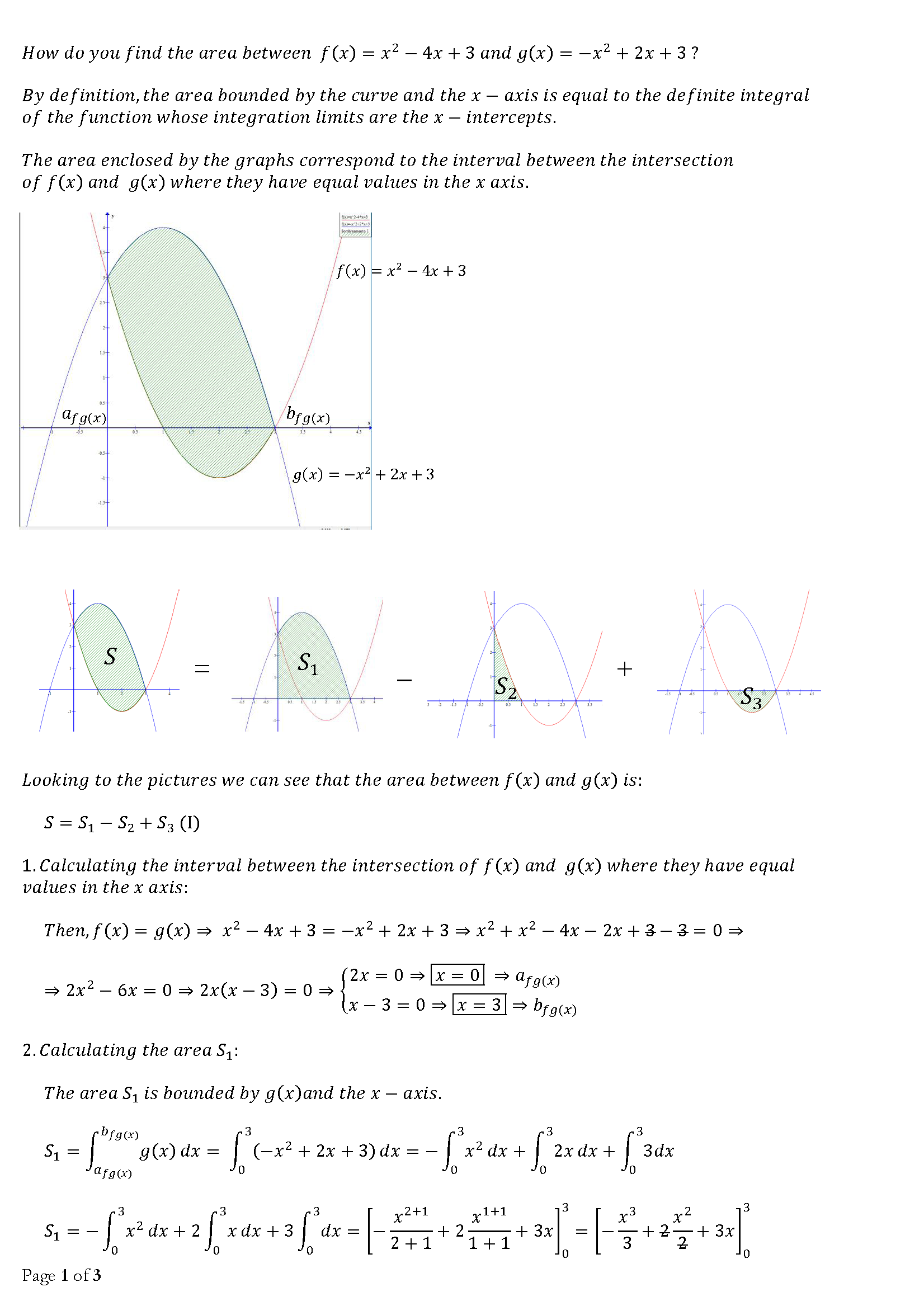



How Do You Find The Area Between F X X 2 4x 3 And G X X 2 2x 3 Socratic
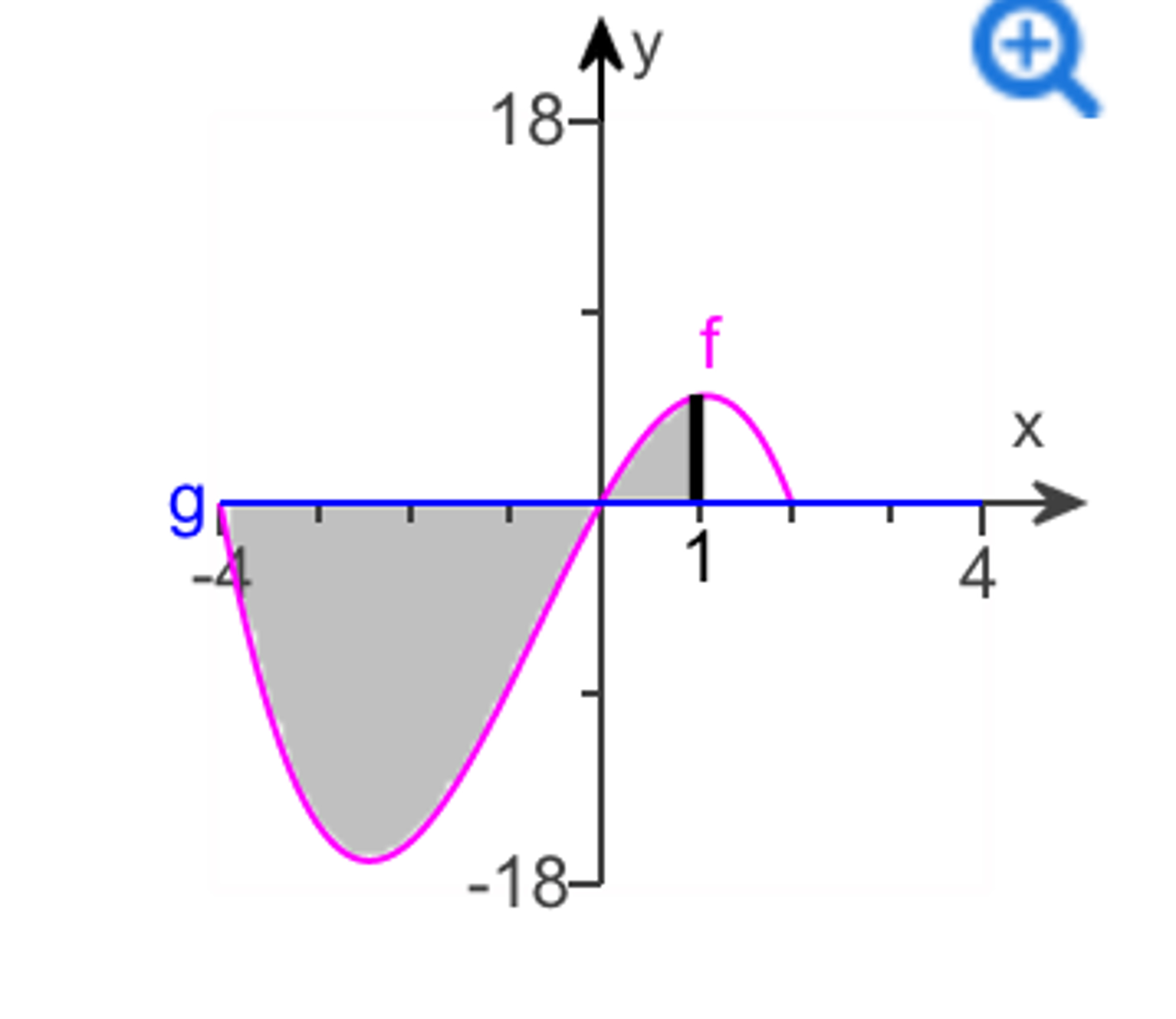



Solved Find The Area Of The Shaded Region F X 8x 2x2 X3 Chegg Com



Solved 1 3 Let F X X2 7 And G X X 3 Find The Chegg Com




If The Function F R Gtr Be Defined By F X 2x 3 And G R Gtr By G X X 3 5 Then Find T Youtube



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿