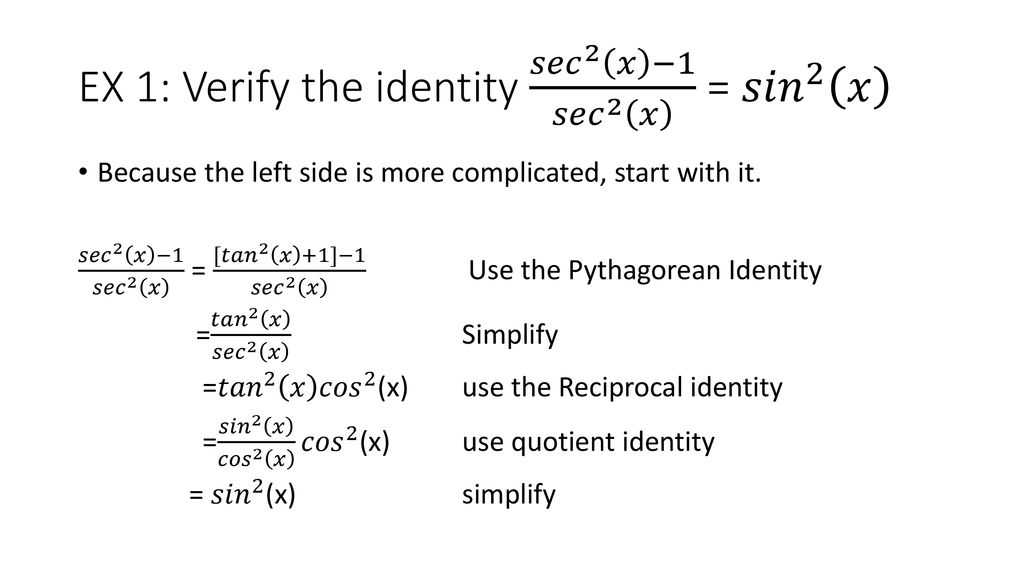
Excellent application of Pythagorean Trig Identities email anilanilkhandelwal@gmailcomMore resources available at wwwmisterwootubecomTranscribed image text Verity the identity tan^2x sin^2 cos^2x = secºx To verify the identity, start with the more complicated side and transform it to look like the other side Choose the correct transformations and transform the expression at each step tan?zx sin 2x cos2x Factor out the greatest common factor Apply a Pythagorean identity to the sum of the second and third term
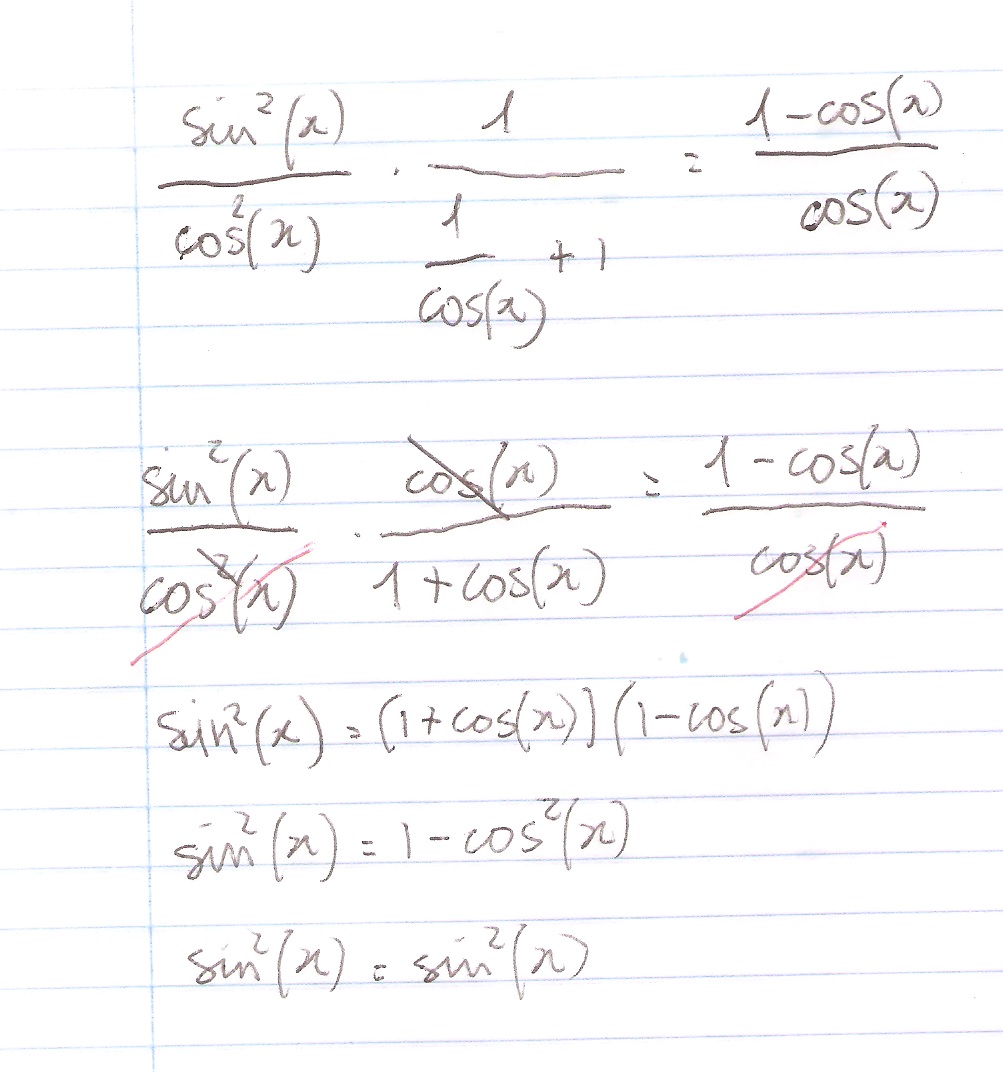
How Do You Prove The Identity Tan 2x Secx 1 1 Cosx Cosx Socratic
What is sec^2x-tan^2x
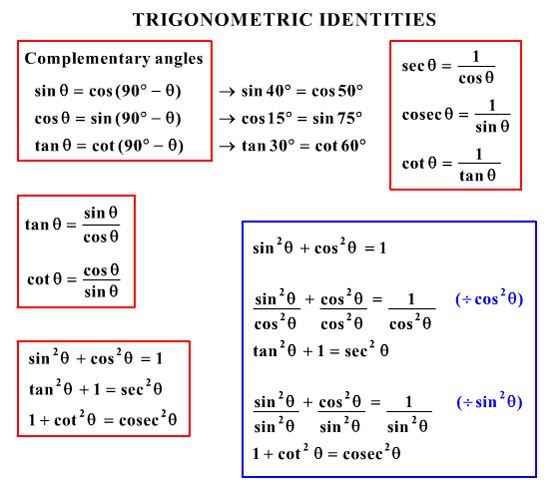
What is sec^2x-tan^2x-Verify the identity sec^2x1tan^2xcosx/cosxcos^2x =tan^2xsecxJan 08, 18 · True Start with the well known pythagorean identity sin^2x cos^2x = 1 This is readily derived directly from the definition of the basic trigonometric functions sin and cos and Pythagoras's Theorem Divide both side by cos^2x and we get sin^2x/cos^2x cos^2x/cos^2x = 1/cos^2x tan^2x 1 = sec^2x tan^2x = sec^2x 1 Confirming that the result is an identity



Derive 1 Tan 2x Sec 2x And 1 Cot 2x Text Cosec 2x Geometrically Mathematics Stack Exchange
In mathematics, trigonometric identities are equalities that involve trigonometric functions and are true for every value of the occurring variables for which both sides of the equality are defined Geometrically, these are identities involving certain functions of one or more anglesThey are distinct from triangle identities, which are identities potentially involving angles but alsoGet an answer for 'Verify the following identity `tanx(cot x tan x) = sec^2x`' and find homework help for other Math questions at eNotes `1/(tan^2x) 1/(cot^2x) = csc^2x sec^2x` 2Trigonometry Trigonometric Identities and Equations Proving Identities 1 Answer Nghi N Sep 13, 16 Prove trig expression Explanation Transform the left side of the expression #LS = sec^4 x
Sec(2x) sec (2 x) Because the two sides have been shown to be equivalent, the equation is an identity tan(2x) cot(2x) csc(2x) = sec(2x) tan (2 x) cot (2 x) csc (2 x) = sec (2 x) is an identitySin 2x, Cos 2x, Tan 2x is the trigonometric formulas which are called as double angle formulas because they have double angles in their trigonometric functions Let's understand it by practicing it through solved example \(Tan 2x =\frac{2tan x}{1tan^{2}x} \)Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with stepbystep explanations, just like a math tutor
Identities Proving Identities Trig Equations Trig Inequalities Evaluate Functions Simplify Statistics Arithmetic Mean Geometric Mean Quadratic Mean Median Mode Order Minimum Maximum Probability MidRange Range Standard Deviation Variance Lower Quartile Upper Quartile Interquartile Range MidhingeHow do you verify the equation is an identity?Identities Proving Identities Trig Equations Trig Inequalities Evaluate Functions Simplify Statistics Arithmetic Mean Geometric Mean Quadratic Mean Median Mode Order Minimum Maximum Probability MidRange Range Standard Deviation Variance Lower Quartile Upper Quartile Interquartile Range Midhinge Standard Normal Distribution


What Is Math Int Tan 2 2x Dx Math Quora


Trig Identities Hsn Forum
Tan^2xtan^2y=sec^2xsec^2y and, how do you factor and simplify, cscx(sin^2xcos^2xtanx)/sinxcosx trigonometry how do i simplify (secx cosx) / sinx?Because the two sides have been shown to be equivalent, the equation is an identity tan2(2x)sin2(2x) cos2(2x) = sec2 (2x) tan 2 (2 x) sin 2 (2 x) cos 2 (2 x) = sec 2 (2 x) is an identityLearn trigonometric identities with free interactive flashcards Choose from 500 different sets of trigonometric identities flashcards on Quizlet Log in Sign up tan^2xsec^2x= 1cot^2x= sin(ab)= 11 csc^2x sinacosbcosasinb sinx^2xcos^2x= 1 tan^2xsec^2x=1



7 4 Proving Trigonometric Identities Mhf4utrigonometry
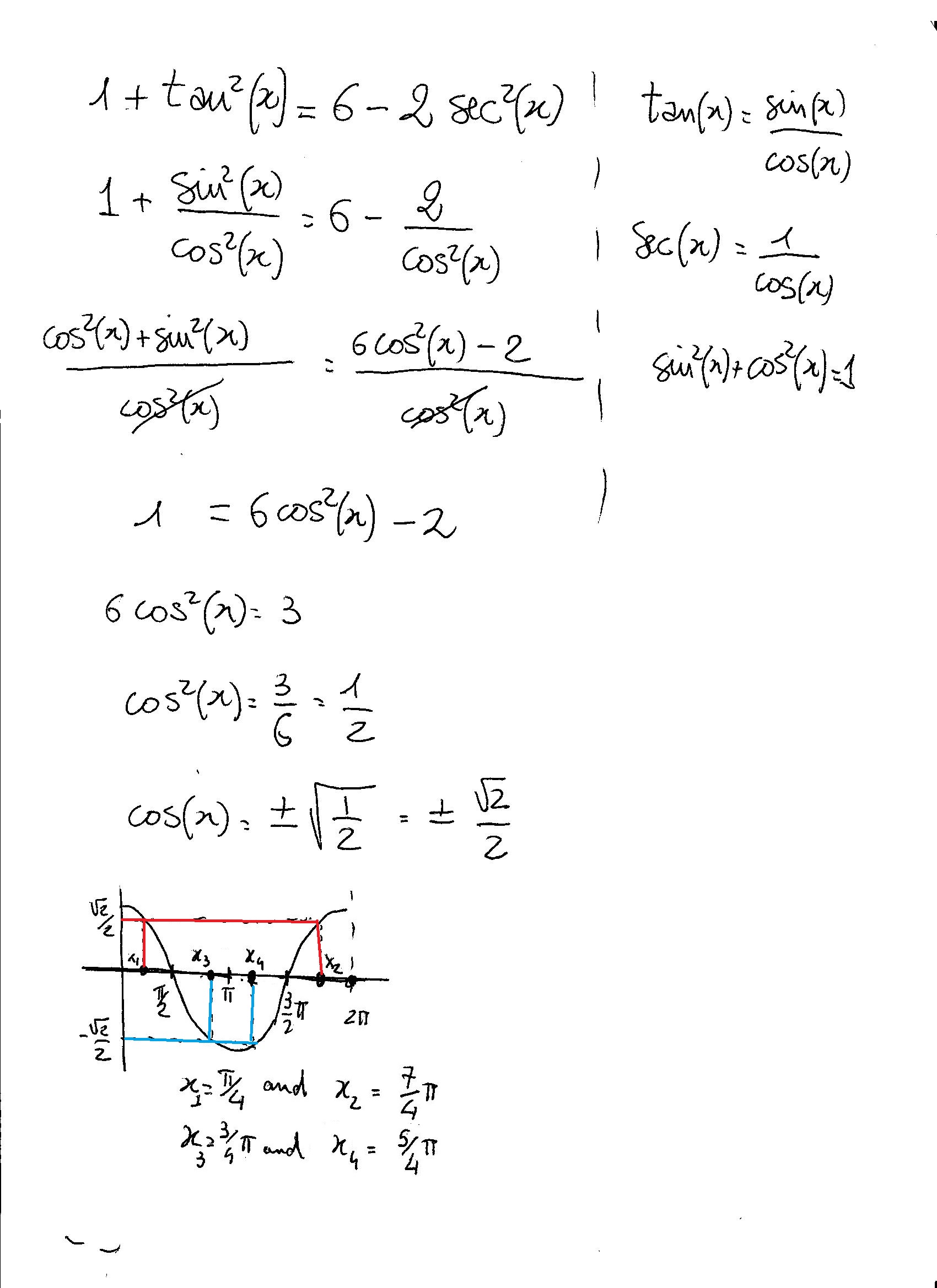


How Do You Solve 1 Tan 2x 6 2sec 2x Socratic
Jul 29, 18 · The trigonometrical identity says 1tan^2x = sec^2 x that means sec^2 x tan^2 x = 1 However in our question, its tan^2 x sec^2 x or say sec^2 x tan^2 x = 1 which is completely against the identity Hense answer is FalseMar 22, 19 · Proving the trigonometric identity $(\tan{^2x}1)(\cos{^2(x)}1)=\tan{^2x}$ has been quite the challenge I have so far attempted using simply the basic trigonometric identities based on the Pythagorean Theorem I am unsure if these basic identities are unsuitable for the situation or if I am not looking at the right angle to tackle this problemFor all values of x Uhm I think false?



Sec 6x Tan 6x 1 2 Tan 2x Sec 2x Important Difficult Trigonometric Identity Youtube



Evaluating Trig Integral Int Tan 3x Sec 2x Dx Mathematics Stack Exchange
See the answer Show transcribed image text Expert Answer 100% (3 ratings)Sec^4x – sec^2x = tan^4x tan^2x'' Answer by Edwin McCravy To do this one we need the identity and its rearranged version Factor common factor out of the left side Replace the first factor on the left, , by Replace the second factor on the left, by Multiply the left side out Reverse the terms on the left EdwinThe figure at the right shows a sector of a circle with radius 1 The sector is θ/(2 π) of the whole circle, so its area is θ/2We assume here that θ < π /2 = = = = The area of triangle OAD is AB/2, or sin(θ)/2The area of triangle OCD is CD/2, or tan(θ)/2 Since triangle OAD lies completely inside the sector, which in turn lies completely inside triangle OCD, we have



Using Trigonometric Identities Video Khan Academy


Trig Identities Hsn Forum
Free trigonometric identities list trigonometric identities by request stepbystep This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience BySo yes, when you originally compared this to the identity you know for secants and tangents, that was how I was thinkingIn this video I go over the proof of the trigonometry identity tan^2(x) 1 = sec^2(x) The proof of this identity is very simple and like many other trig id
x-1=sec(squared)x.jpg)


10 Identity Tan Squared X 1 Sec Squared X Trigonometry Educator Com
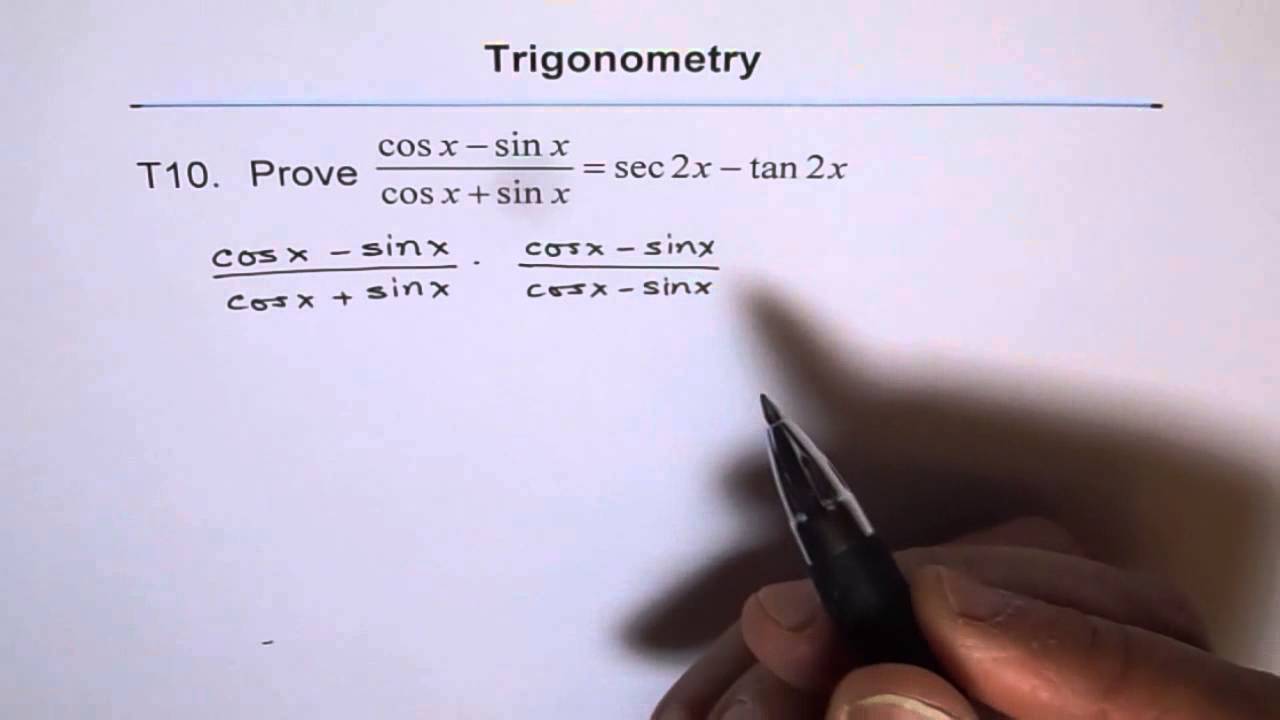


Trig Identity Sec2x Minus Tan2x T10 Youtube
For all values of x tan^2xsec^2x=1 true or false?Nov 12, 15 · I understand identity when it comes to basic equations but this one just goes past my head Thank you for whoever has time for this!Comment I think of the "three identities" as a single identity, which you can manipulate using $\sin^2x\cos^2 x$ into various equivalent forms But thinking about the three identities that you have seen for $\cos(2x)$, let's see which one should be our first pick to manipulate
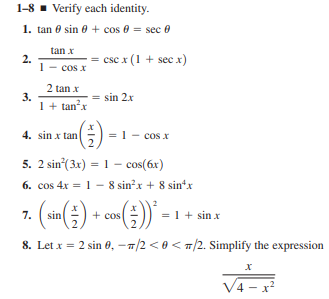


Answered 1 8 Verify Each Identity 1 Tan 0 Bartleby



2sinxcosx Identity Gamers Smart
Identities Proving Identities Trig Equations Trig Inequalities Evaluate Functions Simplify Statistics Arithmetic Mean Geometric Mean Quadratic Mean Median Mode Order Minimum Maximum Probability MidRange Range Standard Deviation Variance Lower Quartile Upper Quartile Interquartile Range Midhinge Standard Normal DistributionFor more resources, visit http//wwwblackpenredpencomTrigverifying trigonometric identities, full playlist https//wwwyoutubecom/playlist?list=PLj7p5OApr 03, 07 · not sure how to start this one, i have tried it a few different ways and i still can't get it (1 tanx)^2 = sec^2x 2tanx



Factor The Expression Then Use Fundamental Identities To Simplify Cos 2x Sec 2x Cos 2x Study Com
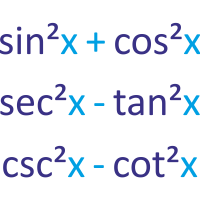


Trigonometric Identities Cheat Sheet Doubleroot In
Simplify the LHS and remember that 1 = sec^2x tan^2x 1 2sinx sin^2x / (cos^2x = 2sec^2x 2secxtanx sec^2x tan^2xMay 07, 15 · tan^2xsec^2x=1 true or false?Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more
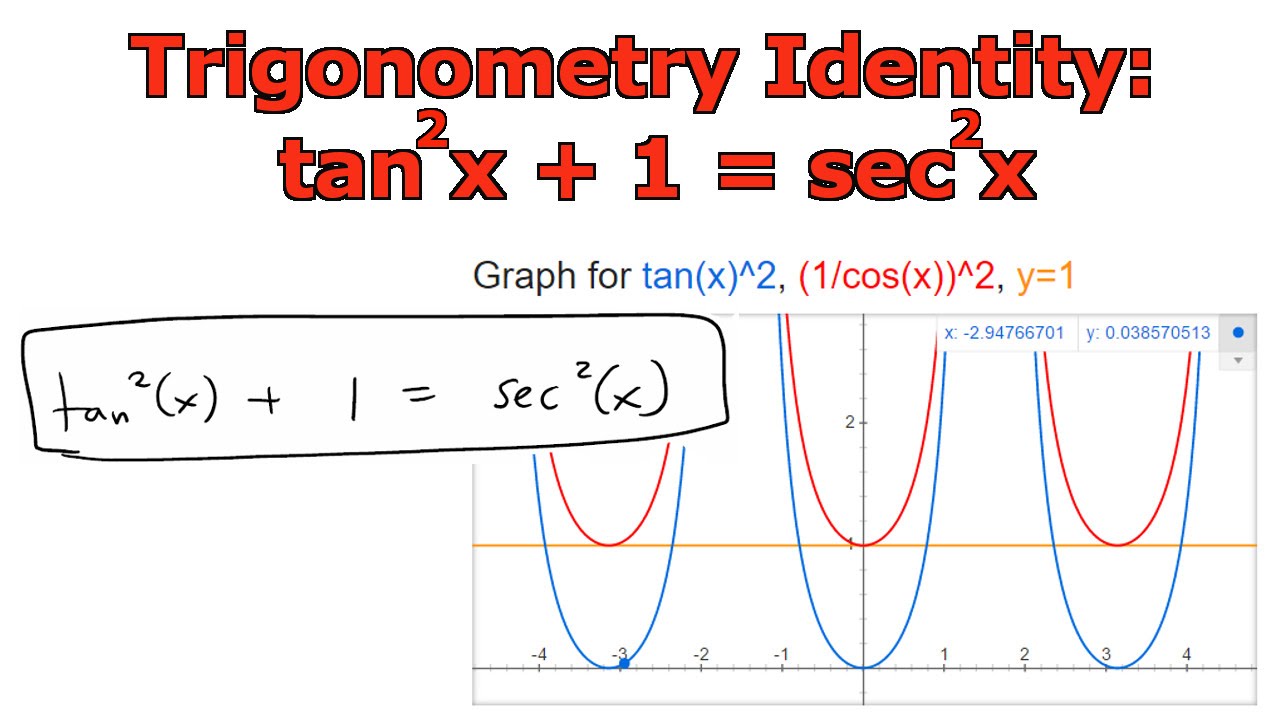


Trigonometry Identity Tan 2 X 1 Sec 2 X Youtube



7 Techniques Of Integration Copyright Cengage Learning All
Sep 13, 16 · How do you verify #Sec^4xtan^4x=sec^2xtan^2x#?Well if nothing else comes to mind try by hand$$\cot^2 x\sec^2x=\frac{\cos^2x}{\sin^2x}\frac 1{\cos^2x}=\frac{\cos^4x\sin^2x}{\cos^2x\sin^2x}$$ and $$\tan^2x\csc^2x=\frac {\sin^2x}{\cos^2x}\frac 1{\sin^2x}=\frac{\sin^4x\cos^2x}{\cos^2x\sin^2x}$$ And these are equal if $$\cos^4x\sin^2x=\sin^4x\cos^2x$$ Now there are various ways to see itYou can put this solution on YOUR website!



Prove The Following Identities I Sec 2x Tan 2xcos Gauthmath



2sinxcosx2 Cos X Answer Gamers Smart
Tan^2 x1=sec^2x So to get 1 on the other side of the equal sign wouldn't it be sec^2xtan^2x=1?Identities Proving Identities Trig Equations Trig Inequalities Evaluate Functions Simplify Statistics Arithmetic Mean Geometric Mean Quadratic Mean Median Mode Order Minimum Maximum Probability MidRange Range Standard Deviation Variance Lower Quartile Upper Quartile Interquartile Range Midhinge Standard Normal DistributionThe Pythagorean identity of secant and tan functions can also be written popularly in two other forms $\sec^2{x}\tan^2{x} \,=\, 1$ $\sec^2{A}\tan^2{A} \,=\, 1$ Remember, the angle of a right triangle can be represented by any symbol but the relationship between secant and tan functions must be written in that symbol



How To Find Tan 2



Lw00plbaiwnh4m
Verify the Identity (sec(x)^2)/(sec(x)^21)=csc(x)^2 Start on the left side Apply pythagorean identity Convert to sines and cosines Tap for more steps Apply the reciprocal identity to Write in sines and cosines using the quotient identity Apply the product rule toI need to prove this identity tan^2xsin^2x = tan^2xsin^2x start with left side tan^2xsin^2x =(sin^2x/cos^2x)sin^2x =(sin^2xsin^2xcos^2x)/cos^2xProve this identity $ \tan(2x)\sec(2x) =\tan(x\pi/4)$ Ask Question Asked 7 years, 1 month ago Active 7 years ago Viewed 3k times 3 $\begingroup$ I've been having a time with this problem I tried to start with the left side but I hit a dead end quick


A Trig Identity



How Many Can You Derive From First Principles Ppt Download
I tried splitting the numerator up so that i had (secx / sinx) (cosx / sinx) and then i changed sec x to 1/ cosx so that i had ((1/cosx)/ sinxQuestion i have to prove this identity 1/ tanx tanx = sec^2x/tanx i do have an idea on what to do but i get stuck every time this is what i did 1/ tanx tanx = sec^2x/tanx cot x 1/ cot x = Found 2 solutions by solve_for_x, Alan3354Question Prove The Identity Sec^2/2 Tan X = Csc 2x This problem has been solved!



Tan2x Tanx Tanx Sec2x Maths Trigonometric Functions Meritnation Com



F 2tanx 1 Tan 2x Cos2x 1 Sec 2x 2tanx 2
Legend x and y are independent variables, ;X tan 2 x = sec 2 x I started this by making sec 1/cos and using the double angle identity for that and it didn't work at all in any way everD is the differential operator, int is the integration operator, C is the constant of integration Identities tan x = sin x/cos x equation 1 cot x = cos x/sin x equation 2 sec x = 1/cos x equation 3 csc x = 1/sin x equation 4


Prove The Identity Tan P 4 X Tan P 4 X 2 Sec 2x Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



Trigonometric Identities Aqa A Level Maths Pure Revision Notes
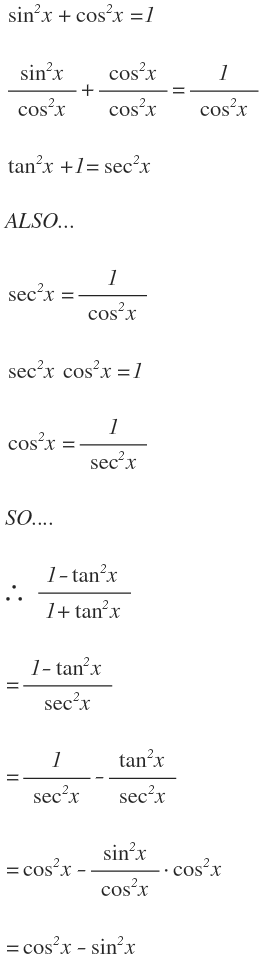


How Do You Simplify 1 Tan 2 X 1 Tan 2 X Socratic



Derive 1 Tan 2x Sec 2x And 1 Cot 2x Text Cosec 2x Geometrically Mathematics Stack Exchange
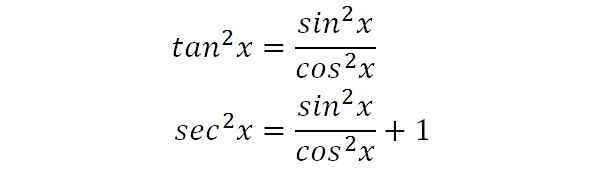


Integrate Sec 2x Method 2



Ex 3 4 8 Find General Solution Of Sec 2 2x 1 Tan 2x Teachoo


Ch Ppt Download



Consider The Following Equations 1 Cosec 2x Sec 2x Cosec 2xsec 2x 2 Sec 2x Tan 2x Sec 2xtan 2x 3 Cosec 2x Tan 2x Cot 2x



Solved Verify The Identity Sec 2 Tanx Sec X Tan X Chegg Com



Solved 2 Prove The Following Trig Identities A Prove T Chegg Com


Trigonometry Reciprocal Identities Expii


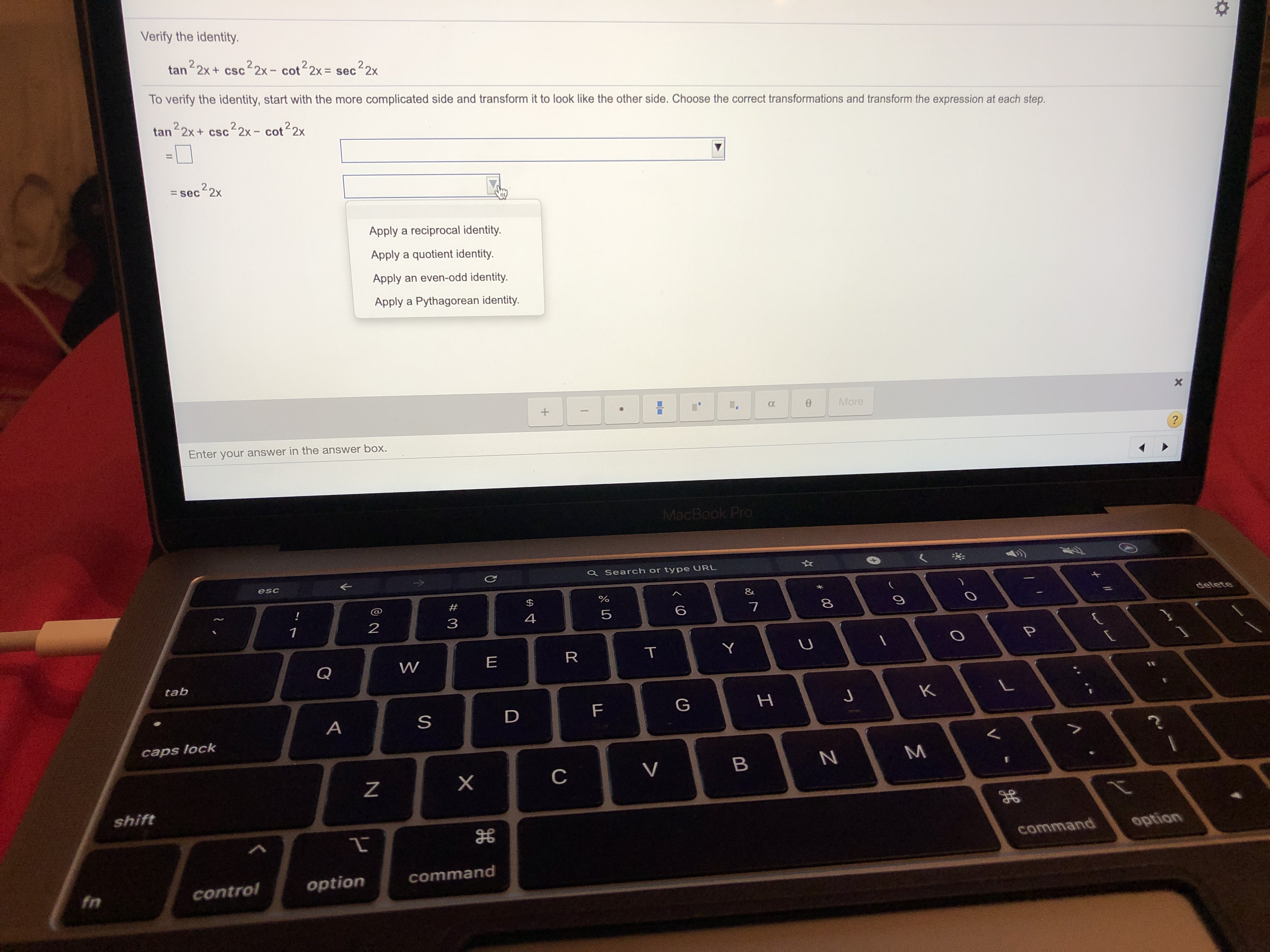
Solved Consider The Possible Identity Tan 2x Cos 2x 1 Cos 2x Sec 2x A State Any Non Permissible Values B Attempt To Verify Possible Identity Course Hero



Is There Any Other Way To Establish This Trig Identity Frac Sec X 1 Tan X Frac Sin X 1 Cos X Mathematics Stack Exchange
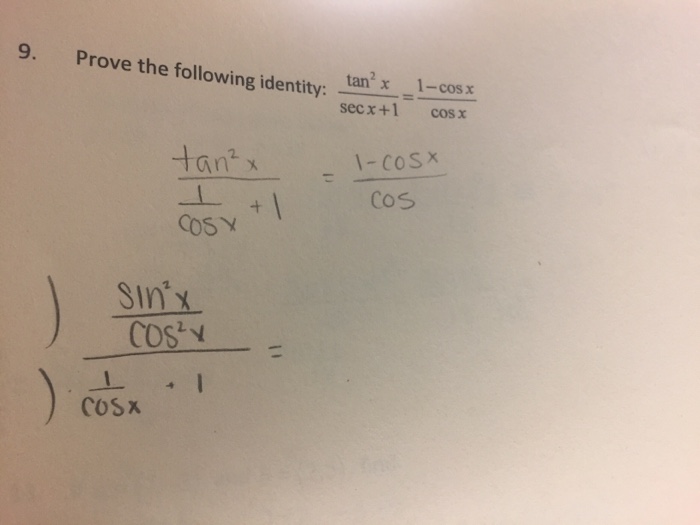


Solved Prove The Following Identity Tan 2 X Sec X 1 Chegg Com



Slides Show
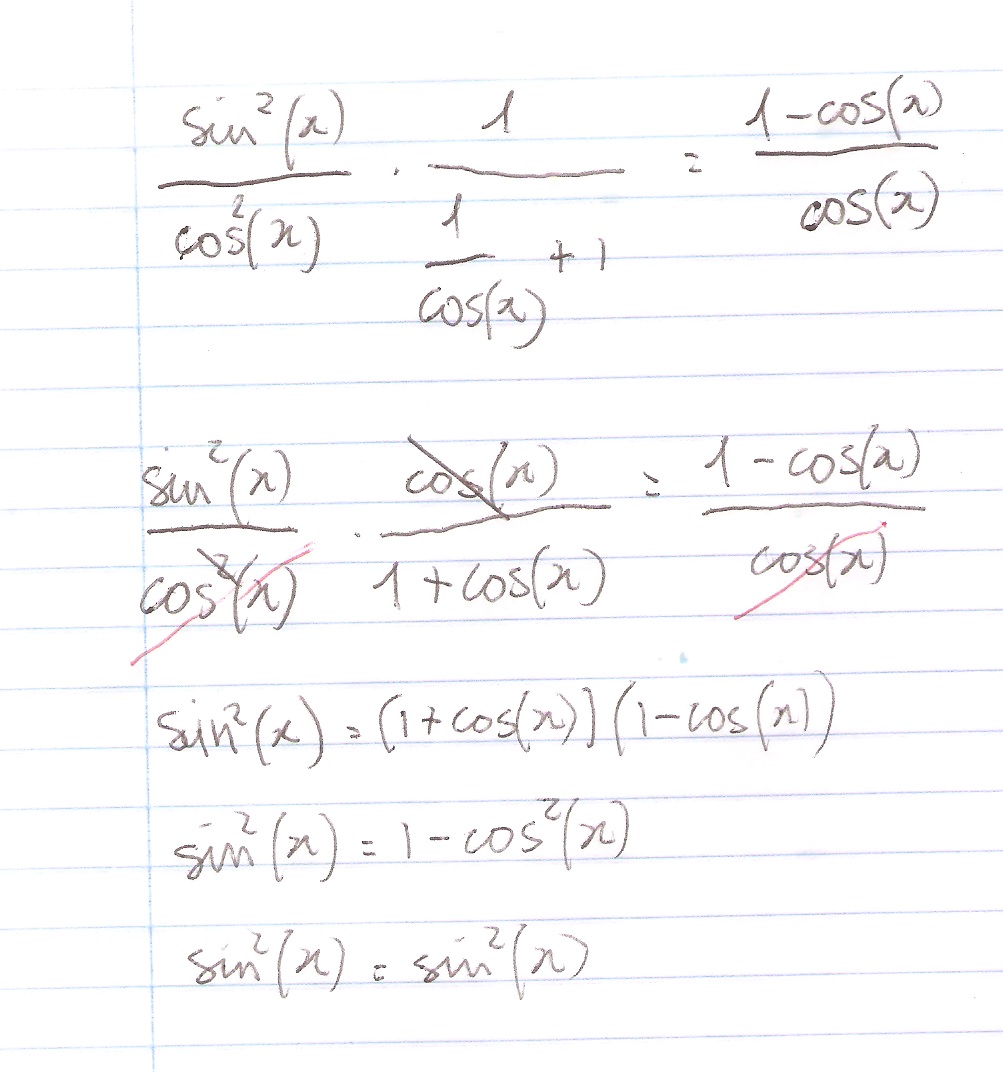


How Do You Prove The Identity Tan 2x Secx 1 1 Cosx Cosx Socratic



9 1 Identities And Proofs Ppt Download



The Derivative Of Sec 2 X With Respect To Tan 2 X Is



Ex 7 3 15 Integrate Tan3 2x Sec 2x Class 12 Ncert Ex 7 3


Solution Tan 2x Secx 1 1 Cosx Cosx Please And Thank You
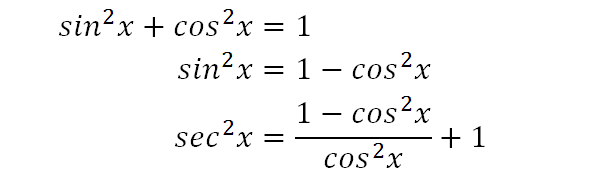


Integrate Sec 2x Method 2


What Would Be Steps In Proving That Tan2x Secx 1 1 Sec X Socratic



Find The General Solution Sec22x 1 Tan 2x Maths Trigonometric Functions Meritnation Com



Trigonometric Identities Aqa A Level Maths Pure Revision Notes



Sample Problems Cos 2 X Tan2 X Tan 2 Csc 2 Tan Sec X Tan X Cos X Sin 4 X Cos 4 X 1 2 Cos 2 X Pdf Free Download



What Is The Integration Of Tan 2x Solution Quora


Solution Verify The Identity By Showing That The Left Equals Right Sec 2x 1 Tan 2 Sec2x Do I Use 1 Cos 2x 1 Tan 2x Or Do I Use 1 Tan 2x 1 Tan 2x Either Way I Do Not Know Where To Go Fro



How Do You Prove Tan 2x Secx 1 1 Secx Socratic



How To Integrate Math Sec 2x Tan 2x Dx Math Quora


Bestmaths Online Proof 4
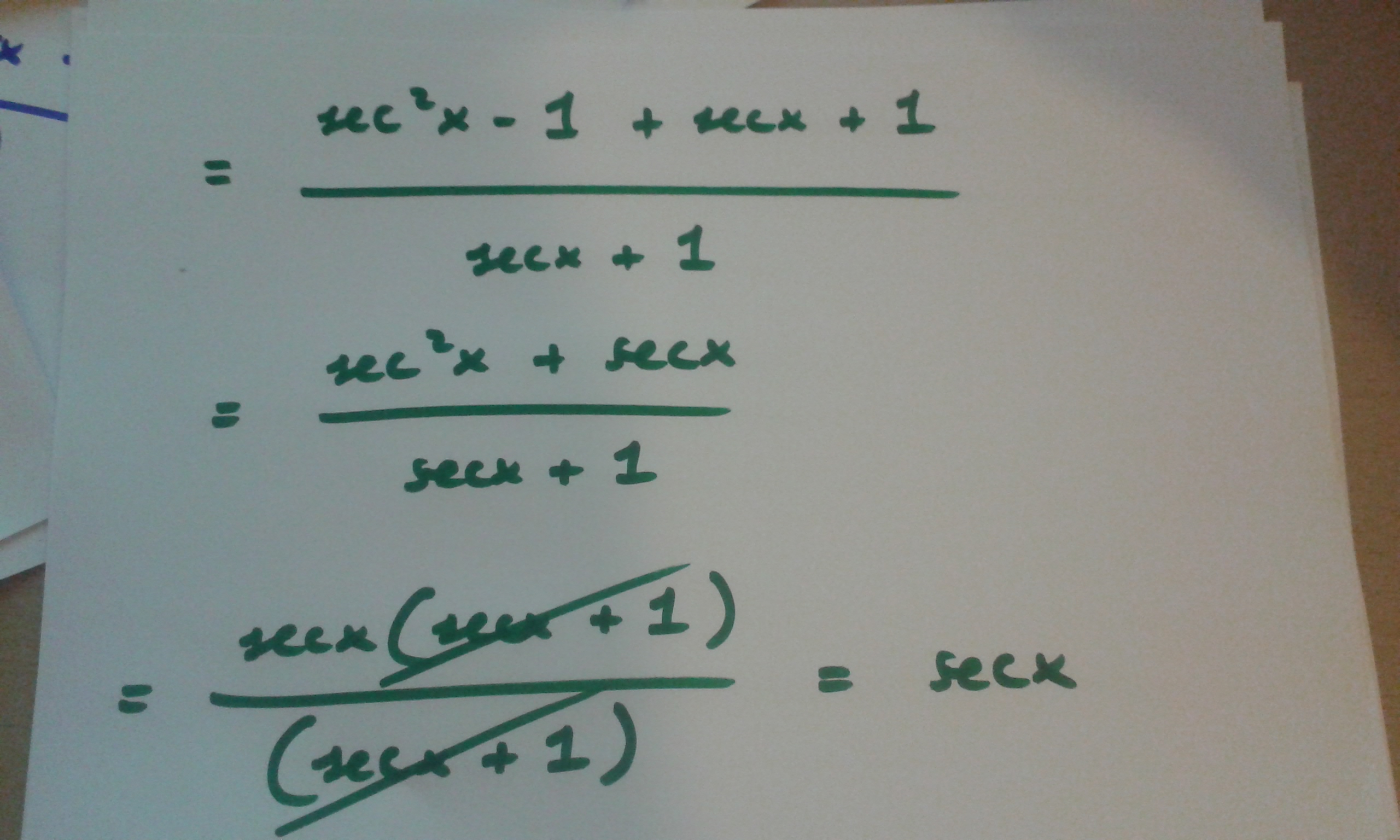


How Do You Prove Tan 2x Secx 1 1 Secx Socratic
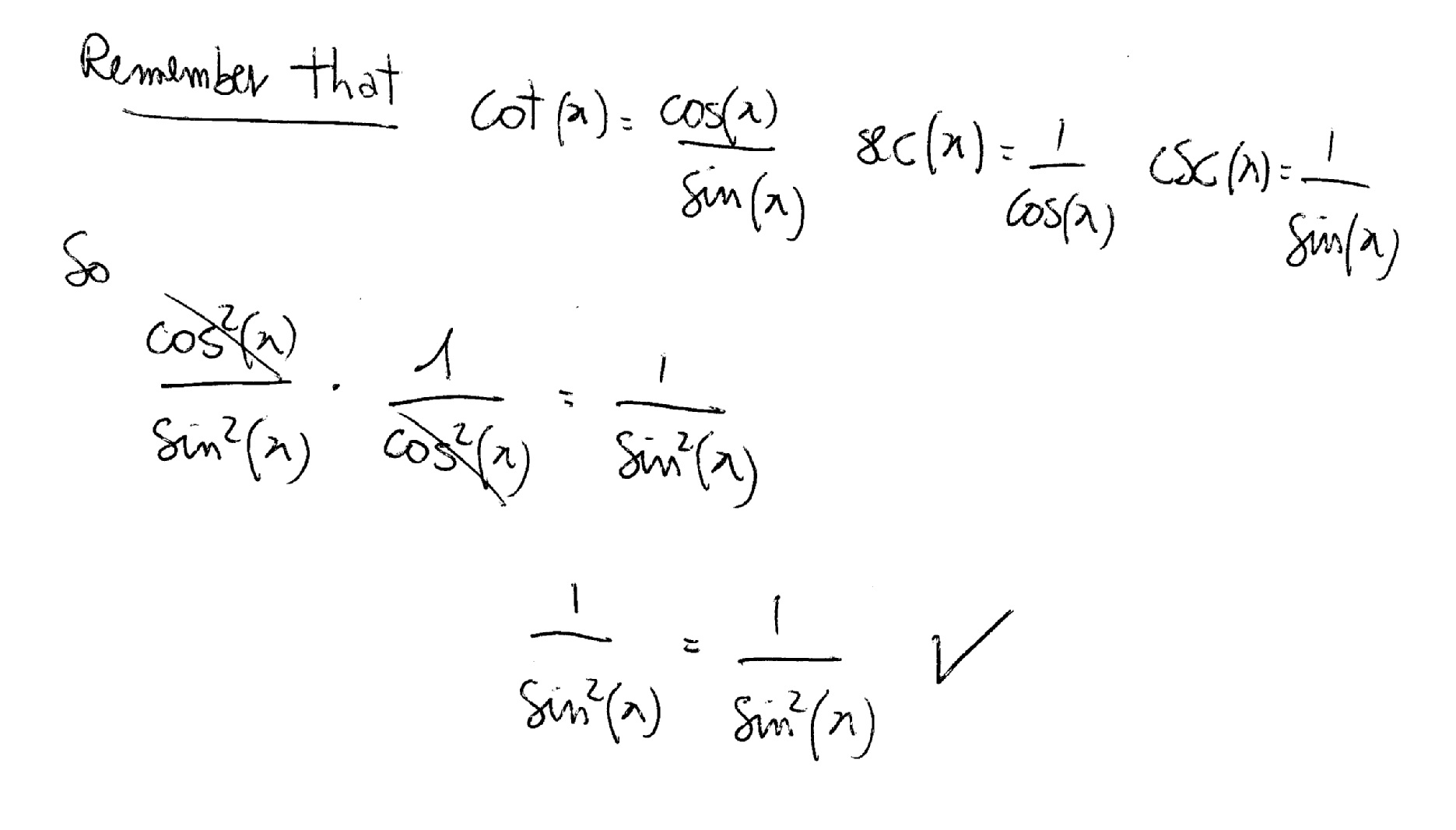


How Do You Verify Cot 2x Sec 2x Csc 2x Socratic



Sec2x In Terms Of Tanx Trig Identity Youtube



Limit Trigonometric Function 2 Sec 2x 1 Tan X Youtube
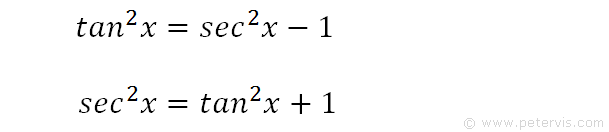


Integrate Sec 2x Method 1



Find The Integrals Of The Functions Tan3 2x Sec 2x Mathematics Shaalaa Com
.JPG)


Every Day I M Calculatin I D3 Unit Q Pythagorean Identities



How Do You Verify 4tan 4 Tan 2x 3 Sec 2x 4tan 2x 3 Kinda Hard Please With All The Steps Thanks Socratic
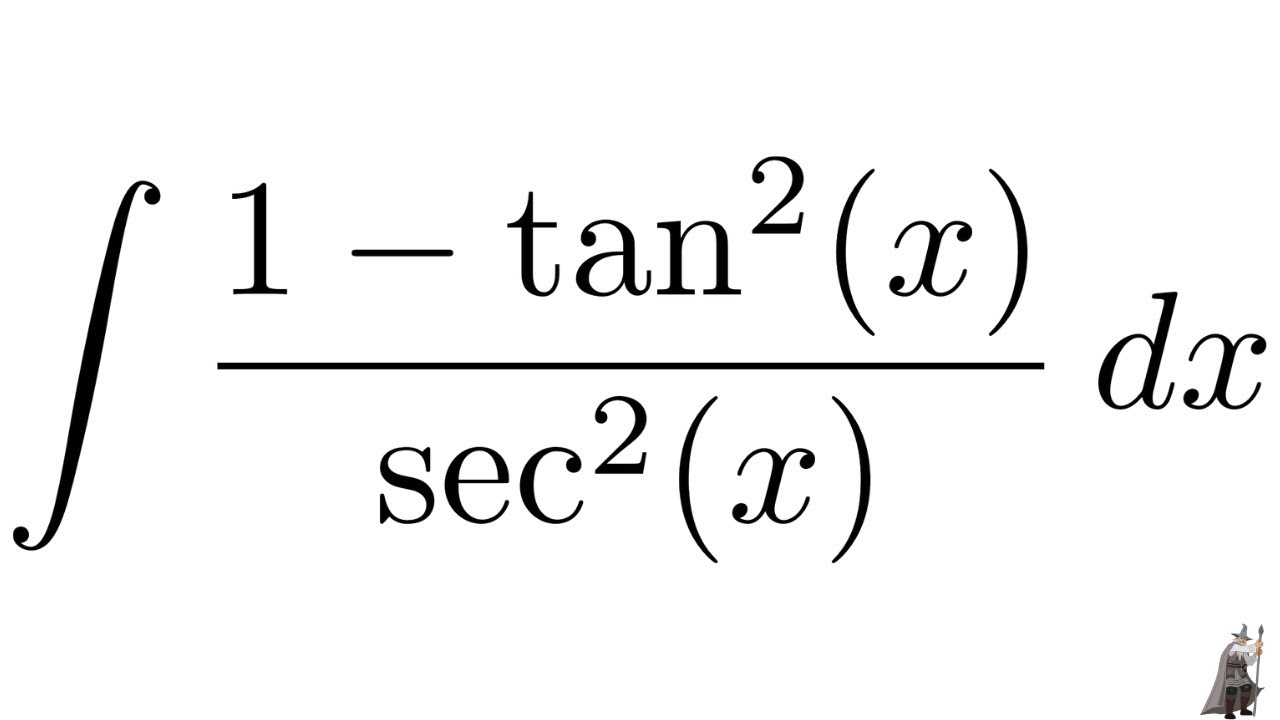


Integral 1 Tan 2 X Sec 2 X Youtube



Verify Each Trigonometric Equation By Substituting Identities To Match The Right Hand Side Of The Brainly Com
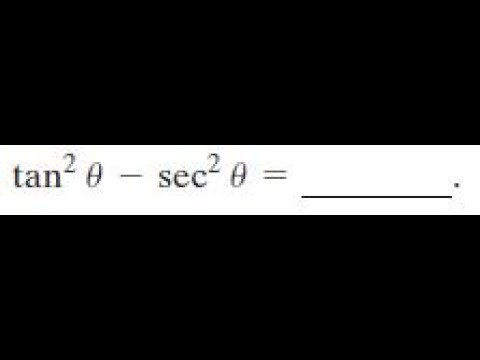


Tan 2x Sec 2x Youtube



1 Cosx 1 Cosx Tan 2x Secx 1 2prove Brainly In



Ex 3 4 8 Find General Solution Of Sec 2 2x 1 Tan 2x Teachoo



How To Find Tan 2 X



Solved Verify The Identity 4 2 Tan X Secx2tan X 1 Whic Chegg Com


Prove The Identity Tan P 4 X Tan P 4 X 2 Sec 2x Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



5 1 Fundamental Trig Identities Sin 1cos 1tan 1 Csc Sec Cot Csc 1sec 1cot 1 Sin Cos Ppt Download



Trig Identity Sec 4x Tan 4x 1 2tan 2x Youtube



How Do You Prove The Identities Cosx Secx Sinx Cscx Sec 2x Tan 2x Socratic
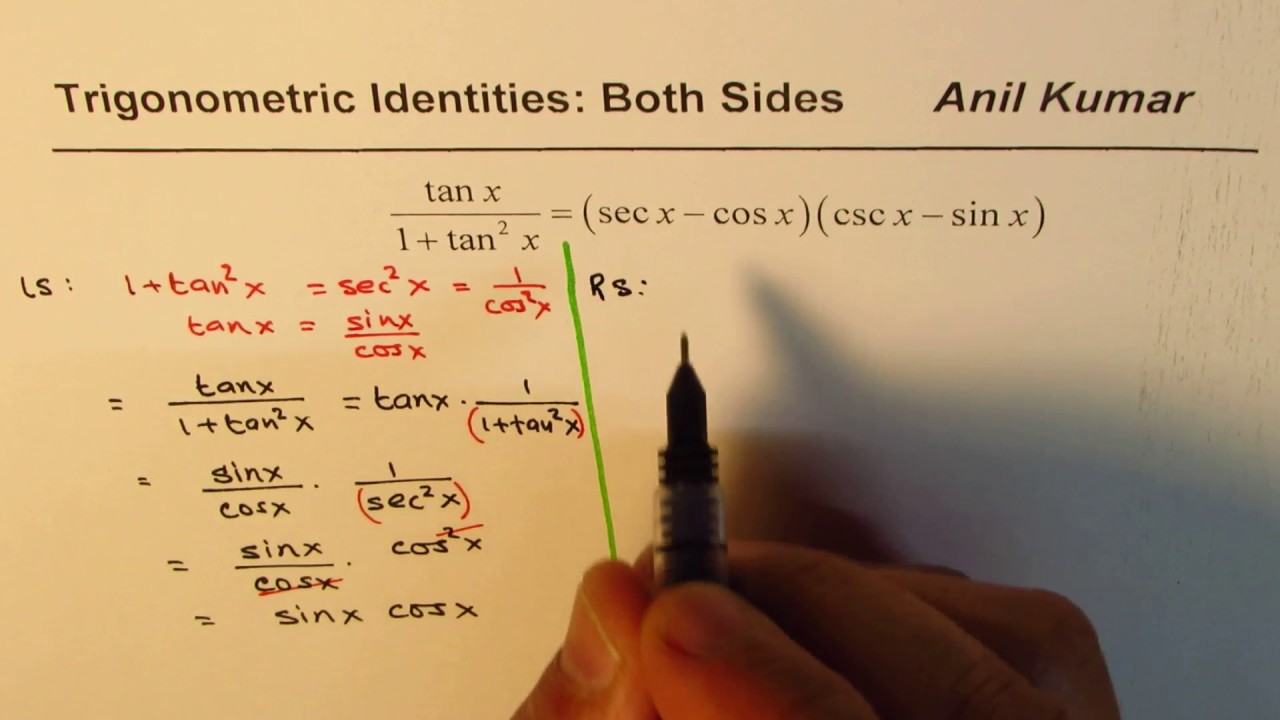


Trig Identity Tan X 1 Tan 2 X Sec X Cos X Csc X Sin X Proved From Both Sides Youtube



7 2 47 Integral Of 1 Tan2x Sec2x Cute766


Solved Prove The Following Trig Identity Sec 2 X 2secx Cosx Cos 2 X Tan 2 X Sin 2 X Course Hero



How To Show That Math Tan 2 X Sec 2 X 1 Math Quora



How Do You Simplify Sec 4x Tan 4x Sec 2x Tan 2x Socratic
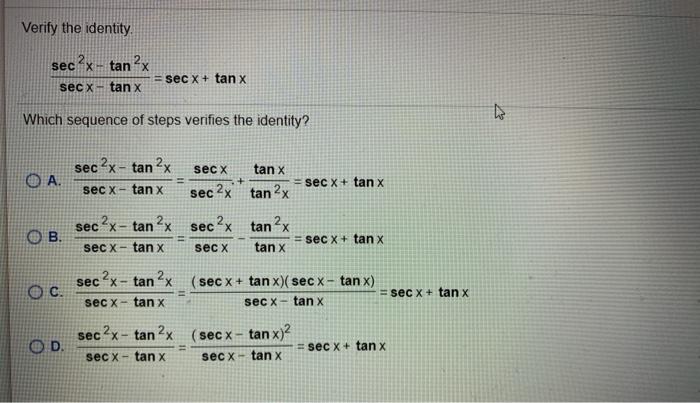


Solved Verify The Identity Sec X Tan 2x Sec X Tan X Se Chegg Com
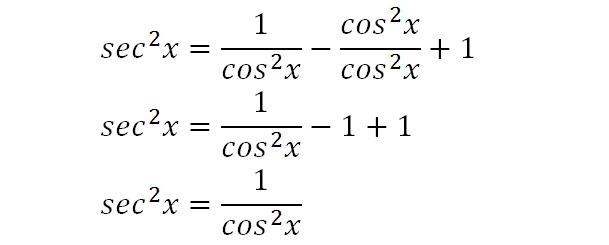


Integrate Sec 2x Method 2


Answered Verify The Identity Tan2x Csc2x Bartleby


Math Problems Simplifying With Trigonometry Identities And Then Integration



Sample Problems Cos 2 X Tan2 X Tan 2 Csc 2 Tan Sec X Tan X Cos X Sin 4 X Cos 4 X 1 2 Cos 2 X Pdf Free Download
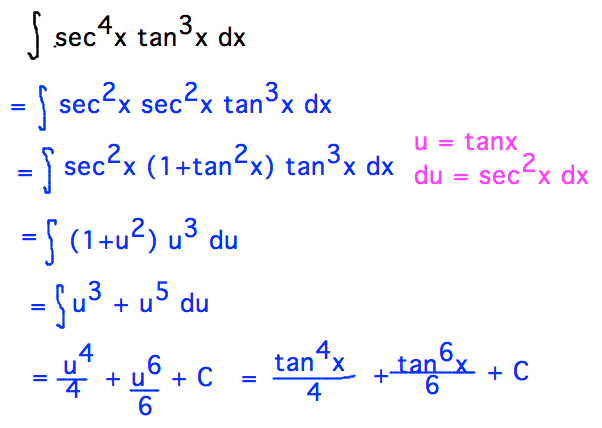


Geneseo Math 222 01 Trigonometric Integration



Answered 3 1 Tanx Tan 2x Sec 2x S Bartleby
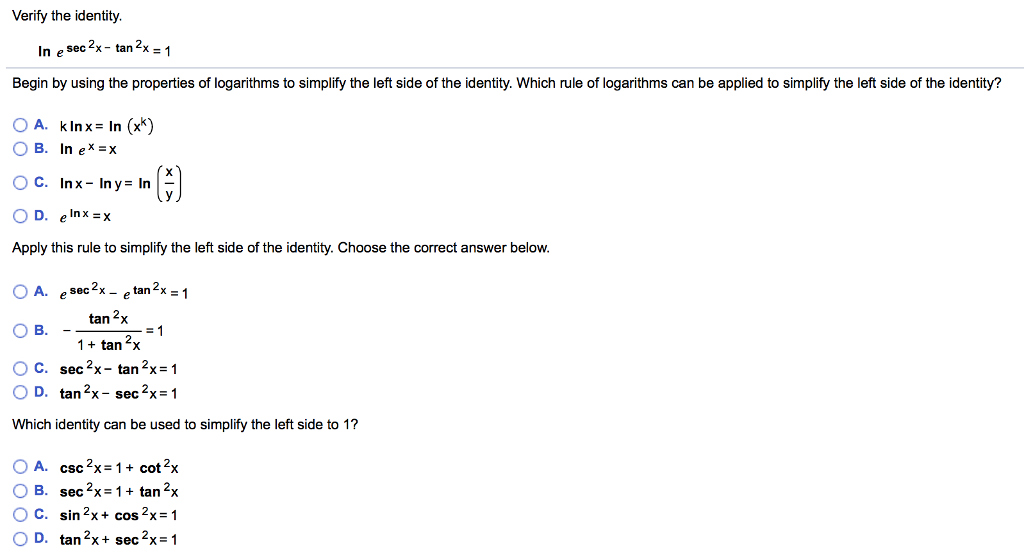


Solved Verify The Identity In Esec 2x Tan 2x 1 Begin By Chegg Com


What Is The Formula Of Tan2x Quora



Cos2x Sin2x 1 1 Tan2x Sec2x Cot2x 1 Csc2x Cofunction


Proof Tan 2 1 Sec 2 Youtube



Which Of The Following Expressions Completes The Identity 1 Sec 2 X Mathematics Stack Exchange


Verifying A Trigonometric Identity Tan 2 X 1 Sec X Sec X Youtube



The Integral Int Sec 2x Secx Tanx 9 2 Dx Equals For Some


View Question Please Help


Chapter 5



What Is The Integral Of Tan 2 X Sec X



Find The Derivative Of The Given Function Y Tan 2x 1 Cot 2x I Tried Converting The Original Function In Terms Of Sin And Cos But It Was Still Too Complicated To Be Called Simplified


Tan2x ただの悪魔の画像



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿